Skip to main content
Samenvatting
- taxonomy
- X. sp.
- unidentified species in genus X
- plural: spp.
- Gram-positive bacteria (GPB)
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Staphylococcus epidermidis
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Streptococcus pyogenes
- Clostridium tetani
- Clostridium difficile
- Bacillus anthracis
- Bacillus cereus
- Listeria monocytogenes
- Enterococcus faecalis
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Corynebacterium diphtheriae
- Gram-negative bacteria (GNB)
- Escherichia coli
- Salmonella spp.
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Vibrio cholerae
- Campylobacter sp.
- Legionella pneumophila
- Proteus mirabilis
- Yersinia pestis
- Helicobacter pylori
- Shigella spp.
1 Intro
- bacterial structure
- cell wall
- capsule
- pili
- flagella
- labs
- general
- techniques
- microscope
- cultures
- PCR
- serology (blood)
- drugs (AB, ...)
- reference labs
- surveillance
- origin of epidemics
- environment samples
- techniques
- whole genome sequencing (WGS)
- seroloprevalentie?
- drug resistance
- infection source
- insects
- lice
- ticks
- fleas
- mosquitoes
- environment
- animals (zoonosis)
- humans
- airborne
- blood
- STDs
- direct contact
- epidemiology
- populations
- susceptibles (S)
- infectives (I)
- removed (R)
- types
- outbreak
- epidemic
- pandemic
- endemic
- One Health
- risk factors
- risk = exposure x low access to prevention/care
- risk = exposure x susceptibility
- pathogenesis
- phases
- colonisation
- adhesion
- invasion
- toxins
- endotoxines
- gram negatief
- deel van celwand
- o.a. lipopolysacchariden (LPS)
- exotoxines
- immune evasion
- intracellular persistance in phagocytes
- antigenic variation
- immunomodulating molecules
- IgA proteases
- voorbeelden
- Brucellosis
- Bacillus anthracis
- anthrax = miltvuur
- transmission: direct contact
- skin infection
- Mycobacterium bovis
- Coxiella burnetii
- Vibrio cholerae
2 Bacteriology
- prokaryotic cell
- capsule
- difficult for AB to penetrate
- can be used as vaccine components
- cell wall
- gram positive
- big layer of peptidoglycan
- contains (lipo-)teichoic acid
- synthesis
- flippase
- PBP = penicillin binding protein
- PBP5: intrinsic resistance to beta-lactam
- PBP2a: acquired resistance (e.g. MRSA)
- PBPs: transglycosylation (link sugars)
- PBPs: transpeptidation (crosslink peptides)
- inhibited by
- beta-lactam AB (via PBP)
- glycopeptide AB (via peptides)
- gram negative
- small inner layer of peptidoglycan
- extra outer membrane (lipid bilayer)
- lipopolysacchariden (LPS)
- special cases
- Mycobacteria
- e.g. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- complex cell wall (incl. capsule)
- regular AB won't work
- use Isoniazid (pro-drug) to treat TBC
- Chlamydia
- cytoplasm
- genetic material
- horizontal gene transfer
- transduction
- via bacteriophages (virusses)
- conjugation
- sex pilus
- transfer plasmid
- transformation
- absorp DNA fragments of dead bacteria
- antibiotics
- Fluoroquinolones
- Rifampicin
- inhibits RNA polymerase
- resistance: rpoB point mutation
- ribosomes
- large subunit
- small subunit
- plasmid
- pili
- flagella
- no mitochondria!
- spores
- examples
- Clostridium difficile
- Clostridium tetani
- Clostridium perfringens
- food intoxication
- Gaz gangrene
- Heliobacter pylori
- urease: urea -> CO2 + NH3 -> increase pH
- breath test with marked urea
- efflux pumps
- respiration
3 Diagnosis en identification
- optical density of sample (urine, CSF, ...)
- techniques
- microscopy
- shapes
- coccus
- diplococcus
- streptococcus: in chains
- staphylococcus: in clusters ("grape-like")
- bacillus
- vibrio: banana
- spirillum
- spirochete
- gram staining
- crystal violet: purple (positive)
- safranin: pink (negative)
- examples
- E. coli
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- gram positive
- diplococcus
- biochemical tests
- old techniques
- take at least 1 day
- antigen-based rapid tests
- cf. pregnancy test
- Clostridoides difficile
- Legionella pneumophila
- MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry
- MALDI = Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization
- TOF = Time of Flight
- most used
- fast
- laser
- electrostatic field
- to accelerate ionized charges
- flight tube
- sample
- matrix
- absorps UV light
- helps ionize the sample
- result: MS profile
- x-axis: m/z
- y-axis: intensity
- match with library of known species
- 16S RNA sequencing
- fallback technique
- 23S: large subunit
- 16S: small subunit
- contains conserved and variable regions
- lookup in "Genbank"
- next generation sequencing: applications
- since 10 years
- metagenomics
- whole genome sequencing (WGS)
- strains
- mutations
- AB effectiveness
- standard panel for GI infections
- parasites
- Gardia
- Antamoeba
- Cryptosporidium
- bacteria
- Clostridium difficile (incl. toxins)
- Campylobacter
- Salmonella
- Yersinia enterocolitica
- viruses
- TBC diagnosis
- Mycobactericum tuberculosis
- grows too slow
- microscopy: special staining
- PCR
- AB
- Isoniazid (specific for mycobacteria)
- Ethambutol
- Rifampicin (mRNA synthesis)
- resistance: rpoB point mutation
- Pyrazinamide (unclear mechanism)
- bacterial meningitis
- causes
- Neisseria meningitidus
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- E. coli
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Listeria monocytogenes
- symptoms
- CSF
- low glucose
- high protein
- cells: polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs)
- bacterial vaginosis
4 DST, PK-PD en TDM
Drug susceptibility testing (DST)
- MIC = minimal inhibitory concentration
- susceptible (S)
- susceptible, increated exposure (I)
- resistant (R)
- natural susceptibility
- acquired resistance
- isoniazid
- pro-drug
- for mycobacteria
- activated by katG?
- INH / inhA (?)
- katG S315T mutation -> resistance
- phenotypic methods
- disk diffusion methods (Kirby-Bauer)
- measure zone of inihibition (mm)
- E test
- strip with increasing concentrations
- Broth microdilution method
- gold standard
- rarely used
- only in reference labs
- grid with increasing concentrations
- breakpoint concentrations
- only low+high concentrations instead of all in between
- 0/0 -> R
- 0/1 -> I
- 1/1 -> S
- alternative methods
- enzymatic
- fast, does not require overnight incubation
- PCR
- sequence-based detection
- Rifampicin resistance determining region (RRDR)
- whole genome sequencing (WGS)
Pharmacokinetics (PK)
- AB concentration
- oral intake
- 0 -> peak
- peak -> 0
- variable (depends on half life)
- example: longer in urine than in blood
- window above MIC
Pharmacodynamics (PD)
- AB dependent PK activity
- concentration dependent
- Amikacin (aminoglycoside - small subunit ribosome)
- measure: Cmax
- higer = more side effects
- time and concentration dependent
- Vancomycin (non lactam > glycopeptide)
- measure: AUC above MIC
- time dependent
- Cephalosporins (beta-lactam)
- measure: time above MIC
- treatment regimen
- new intake when below MIC
- infusion: bolus vs continuous
Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM)
- therapeutic window
- between %cured and %side effects
- Amikacin
- concentration dependent
- next dosis when C < 1 mg/ml (otherwise toxic)
- drug interactions
- influence of cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP)
- CYP inhibitor -> less AB degradation/elimination
- how to measure AB concentration in blood
- liquid chromatography
- ELISA
5 Antibiotics and Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
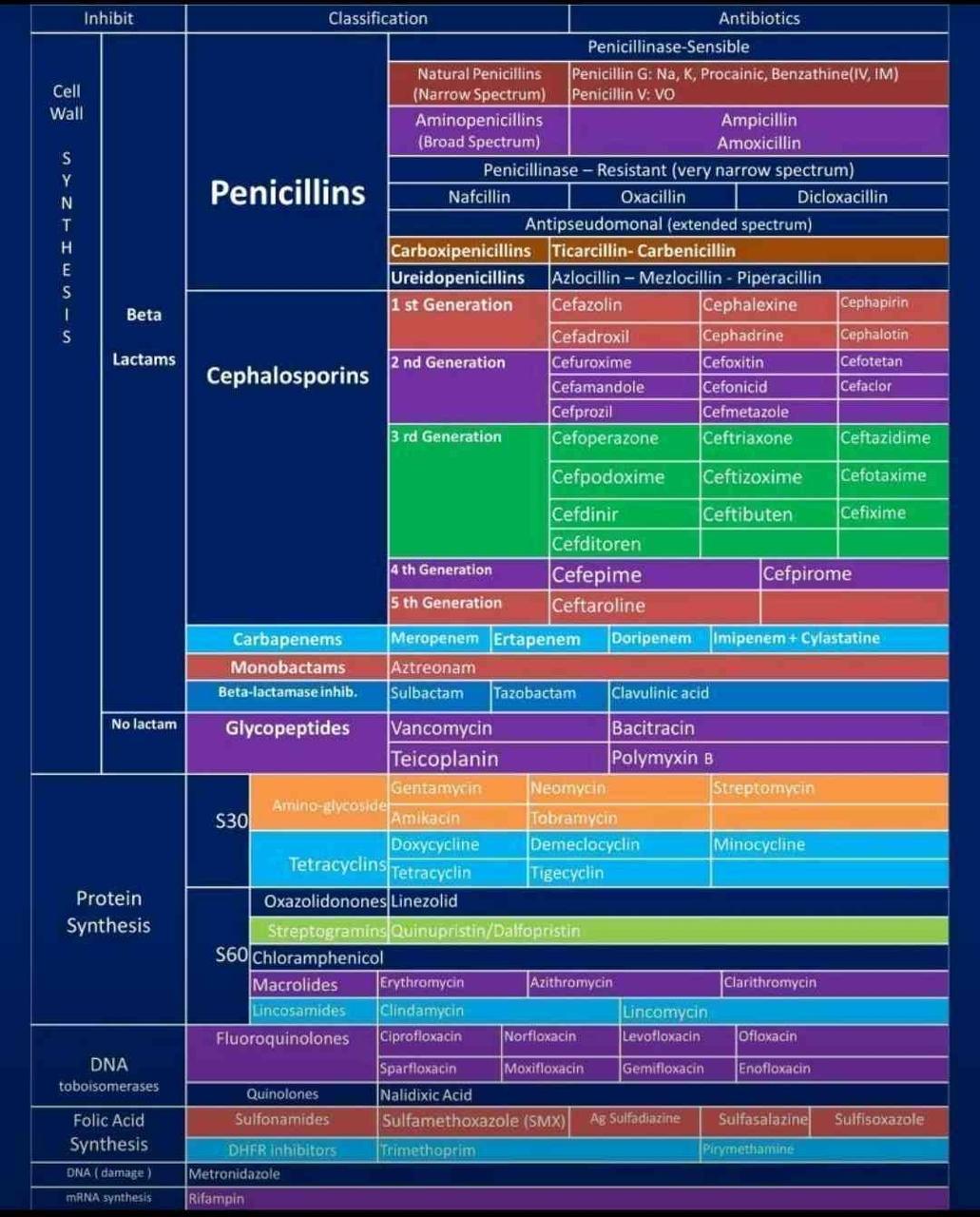
- 1928: discovery Penicillin (Fleming)
- 1940: production Penicillin
- 1943: Streptomycin
- 1950-60: golden age
- AB mechanisms
- cell wall
- non lactam
- glycopeptide (via peptides)
- Vancomycin
- works well against Gram positives
- too big to cross outer membrane of Gram negatives
- VRE = Vancomycin resistant enterococcus
- beta-lactam (via PBP)
- affects transpeptidation via PBPs
- allergies
- examples
- Penicillins
- Cephalosporins
- 1st gen
- 2nd
- 3rd
- 4th
- (5th)
- Carbapenems
- Monobactams
- resistance
- PBP5: intrinsic resistance
- PBP2a: acquired resistance (e.g. MRSA)
- mecA gene
- solution: use Vancomycin
- Mycobacteria (e.g. TBC)
- Chlamydia
- wall-less
- use TODO -> doxycycline (S30)?
- penicillinase / beta-lactamase
- sensitive
- resistant
- methiciliin
- flucloxacillin
- DNA
- Metronidazole (pro-drug)
- only anaerobic bacteria and protozoa
- activated in anaerobic environments
- C. difficule
- Trichomonas
- Entamoeba
- Giardia
- DNA replication
- RNA polymerase
- Rifampicin / Rifampin
- resistance: rpoB point mutation
- ribosomes
- large subunit (S60)
- Macrolides
- (Azithromycin)
- (Clarithromycin)
- Lincosamides
- small subunit (S30)
- Aminoglycosides
- Tetracyclines
- folic acid synthesis
- Sulfonamides
- Trimethoprim
- (bacterio)phage therapy
- AMR
- overuse
- incorrect use
- WHO prio
- 1 critical
- 2 high
- 3 medium
- mainly community acquired
- mechanisms
- decreased intracellular concentration
- target modification
- absence
- mutation
- alternative pathway
- increased expression
- enzymatic degradation
6 Vaccines
Live attenuated vaccines
- old technique: heating
- Vibrio cholerae
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- BCG vaccine
- based on M. bovis
- low virulence in humans
- cross-immunity with M. tuberculosis
- culture on bile salts (stress) -> loss of virulence
- Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhi
- types of salmonella
- S. Typhi (vaccine)
- typhoid fever
- adhesion to M cells and Peyer patches in gut
- diffusion via lymph
- to liver and spleen, bone marrow
- Non-typhoidal salmonella (NTS) (no vaccine)
- gastero-enteric disease
- invasive disease
- Bacillus anthracis
Toxoid vaccines
- harm caused by toxins instead of bacteria
- formaldehyde treatment
- DTaP vaccine
- Diphtheria
- Corynebacterium diphtheriae
- causes necrosis in pharynx
- Tetanus = kaakklem
- Clostridium tetani
- spores are everywhere (in soil, ...)
- Pertussis = kinkhoest
- Bordetella pertussis
- droplet transmission
- whole cell vaccine (DTP)
- more effective
- side effects
- acellular vaccine (DTaP)
- typically diagnosed only after infectious phase
- vaccinate
- during pregnancy (3rd trimster)
- 8 weeks
- 4, 6, 18 months
- 4 years
- ~13 years
- repeat every 10 years
Polysaccharide and conjugated vaccines
- polysaccharide
- antigens on cell wall hidden by polysaccharides in capsule
- Capsular Polysaccharide (CPS)
- different versions are called serotypes
- CPSs can be used as vaccine components
- meningitis
- bacterial or viral
- bacterial: neutrophiles in CSF
- viral: lymphocytes in CSF
- symptoms
- red rash
- doesn't fade when you press a glass against it
- fever
- vomiting
- headache
- neck stiffness
- light sensitivity
- lethargy
- in subarachnoid space
- contains CSF
- lumbar punction
- low glucose
- high protein
- cells: polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs)
- makes CSF look turbid instead of clear
- caused by many pathogens

- treatment
- Penicillin / Amoxicillin
- Ceftriaxone
- Vancomycin
- E. coli
- Listeria monocytogenes (LM)
- mostly in newborns and adults
- S. agalactiae (group B = GBS)
- S. pneumoniae (SP)
- not in newborns
- non-invasive pneumococcal diseases
- invastive pneumococcal diseases (IPD)
- causes
- meningitis
- sepsis
- complicated pneumonia
- 100+ serotypes
- incidence increases with age
- seasonal
- vaccine (pneumococcus)
- details: see infectieziekten
- for adults: without carrier protein
- B cell + plasma cell response
- for children: with carrier protein
- Haemophilus influenzae
- uncapsulated types (no vaccine)
- encapsulated types
- type b (Hib vaccine)
- very low incidence since vaccine
- causes
- meningitis
- epiglottitis (exam!)
- risk of suffocation in children
- sepsis
- pneumonia
- Neisseria meningitidis (NM)
- mostly in children
- droplet transmission
- often: colonization (in nasopharynx) without symptoms
- bad luck: gets in bloodstream
- "meningitis belt" in Africa around equator
- ACWY vaccine
- protects against four major serotypes (with different CPS)
- not included: B, X
- not used in Belgium
- alternative vaccine using other targets
Vaccine program in Belgium
- ignoring viruses
- diphteria, kinkhoest, tetanus (DKT)
- Haemophilus influenza b
- Meningokokken C
- pneumokokken
7 Skin and soft tissues
- TODO
- exam: focus on most frequent pathogens and diseases
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Streptococcus pyogenes (GAS)
8 Airways
9 UTIs and STDs
Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- symptoms
- frequent urge
- pain during urination
- cloudy urine
- more common in women
- extra risk: katheter
- upper UTI
- kidneys: pyelonephritis
- ureters: ureteritis
- lower UTI
- bladder: cystitis
- symptomatic
- asymptomatic
- still requires treatment in pregnant women
- prostate: prostatitis
- enlarged
- compresses urethra
- makes cystitis even worse
- urethra: urethritis
- urine sample
- process
- wash hands
- use sterile cup
- wipe genitals
- midstream
- first part will contain skin pathogens
- send to lab quickly
- result
- in healthy people mostly sterile liquid
- pyuria: white blood cells in urine
- bacteriuria
- tests
- microscope
- dip sticks
- test for E. coli (gram negative)
- won't test for enterococcus
- semi-quantitative
- grow culture from standardized volume
- verify that it is a single bacteria
- count colony forming units (CFUs)
- uropathogens
- enterobacteria
- E. coli (majority)
- Klebsiella
- Proteus
- Enterobacter
- ...
- Enterococcus sp
- S. saprophyticus
- treatment
- UTI
- special oral AB
- duration: few days
- nitrofurantoine
- fosfomycine
- acute prostatitis
- oral AB
- duration: few weeks
- levofloxacine
- ciprofloxaxine
- acute pyelonephritis
Special cases
- catheter-associated UTI (CAUTI)
- extra risk: some urine remains in bladder (stasis)
- different set of pathogens
- E. coli
- Enterococcus spp
- S. aureus
- Candida spp
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Klebsiella pneumonia
- UTI during pregnancy
- urine test during every checkup
- foetus presses on bladder
- UTI during childhood
- taught to keep urine up
- recurrent
- vesico-uretric reflux
- risks kidney damage
- requires treatment
- UTIs and DM2
- complicated UTI
- more frequent
- more severe course
- unusual bacteria (not E. coli) more common
- factors
- glucosuria
- vascular complications
Chorioamnionitis and neonatal meningitis
- neonatal meningitis
- aquired in utero or during childbirth
- caused by beta-hemolytic streptococci
- Lancefield classification
- group A streptococcus (GAS) = Streptococcus pyogenes
- group B streptococcus (GBS) = Streptococcus agalactiae
- early onset disease (EOD)
- late onset disease (LOD)
- both can cause
- sepsis
- pneumonia
- meningitis
- chorioamnionitis
- caused by vaginal flora
- causes inflammation in mother and foetus
- can cause preterm birth
- difficult to diagnose
- test: amniotic fluid sample
Sexually transmissed diseases (STDs)
- STDs in Belgium
- male > female
- mostly in heteros or MSM
Gonorrhoea
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- not to be confused with N. meningitidis causing meningitis
- symptoms
- fever
- pain
- in newborns
- sepsis
- arthritis
- meningitis (only in newborns!)
- prevention: routine screening for STDs during pregnancy
Chlamydia
- C. pneumoniae
- atypical "walking" pneumonia
- C. psittaci
- C. trachomatis
- serovars
- A-B
- transmission: direct contact (not STD)
- main cause of blindness in developing countries
- D-K (most common)
- urethtritis
- PID (see below)
- neonatal pneumonia
- neonatal conjunctivitis
- L1-L3
- in subtropical areas
- more virulent
- infects
- lifecycle
- outside of cell
- inside of cell
- treatment
- beta-lactam won't work due to special cell wall
Syphilis
- first stage: ulcer (painless)
- secondary stage: rash
- typical symptom: spots on hands
- tertiary stage: internal organs?
- diagnosis
- cultures don't work well
- PCR does not work well
- serology
- complex diagnosis (examen!)
- treponemal antibodies
- test remains positive even after treatment
- non-treponemal antibodies after treatment
- treatment: AB (penicillin, beta-lactam)
- congenital syphilis
- test mother during pregnancy
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Mycoplasma genitalium
- limited clinical symptoms
- distorted falopian tubes
- treatment
- no cell wall
- beta-lactams don't work
- macrolides
Screening
- pregnant women
- N. gonorrhoeae
- syphilis
- ..?
- asymptomatic with higher risk
- PCR
- C. trachomatis
- N. gonorrhoeae
- symptomatic
- PCR
- C. trachomatis
- N. gonorrhoeae
- Mycoplasma genitalium
- Trichomonas vaginalis
10 Gastro-intestinal infections
- diarrheal diseases
- (clean) water, sanitation, hygiene (WASH)
Food intoxication
- bacteria die when cooking food
- their toxins can remain stable
- Staphylococcal food poisoning (SFP)
- Clostridium botulinum
- Gram positive
- spores
- anaerobic in food jars
- neurological symptoms
Gastric and duodenal ulcers
- Helicobacter pylori
- transmission
- uses urease to produce NH3 + CO2 from urea
- NH3 protects against low pH
- symptoms
- stomach ulcer
- stomach bleeding
- diagnosis
- biopsy
- breath test
- drink marked urea
- processed by bacteria using urease
- detect marked CO2 in breath
- treatment
- long term: can cause cancer
Gastro-intestinal infections
- Campylobacter sp.
- from chickens
- mild gastro-enteritis
- diarrhea
- E. coli
- pathotypes
- Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) = traveler's diarrhea
- enterotoxin
- gut releases water and electrolytes
- Enterophatogenic E. coli (EPEC)
- no toxin
- disturb villi
- disturb tight junctions
- Enterohemorragic E. coli (EHEC)
- toxin
- affects endothelial cells in blood vessels
- thrombus
- often infected during industrial food processing
- Enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC)
- destroys colon epithelium
- synonym: Shigella?
- Clostridoides difficile
- Gram positive
- spores
- anaerobic
- existing gut flora inhibit these spores
- die when taking AB -> dysbiosis
- toxins
- toxin A
- toxin B
- colon inflammation
- outbreaks in hospitals
- spores survive typical cleaning products
- treatment
- AB: vancomycin
- big glycopeptide
- typically given via IV because of poor absorption
- here given orally
- high dose in gut
- low dose in blood
- Vibrio cholerae
- aquatic environment
- heavy diarrhea
Foodborne infections causing systemic diseases
- Salmonella
- S. Typhi
- gastero-enteric symptoms
- typhoid fever (systemic)
- physiopathology
- M cell / Peyer patch invasion
- spreads via blood to liver, spleen, bone
- re-expose Peyer patches via bile
- "wasting disease": patients waste away
- transmission
- Non-typhoidal (NTS)
- gastero-enteric symptoms
- systemic: less frequent
- Yersinia sp.
- Gram negative
- Yersinia pestis -> plague
- type 3 secretion system
- "syringe" on outer membrane bacteria
- injects toxins
- Yersinia enterocolita
- pseudo-appendicitis
- infects lymph node next to appendix
- diarrhea
- weeks later: red patches on skin
Listeria monocytogenes
- transmission
- contaminated food
- unpasteurized milk, cheese
- affects
- gut
- liver
- spleen
- brain (in weak an elderly)
- placenta
- change diet when pregnant
11 Bones and joints
Osteomyelitis
- ends of long bones
- hematogenous: spread by blood
- bone is "eaten"
- take long to develop
- pus searches way out
- pathogenesis
- high virulence / rapid onset
- S. aureus
- beta-hemolytic streptococcus
- gram negatives (Salmonella)
- low virulence / late onset
- CNS
- Streptococcus viridans
- Cutibacterium acnes
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- vertebra -> spinal tuberculosis (Pott's disease)
- often due to infected prothesis
- nerve problems
- can't feel pain
- patients get more lesions
- vascular problems
- ulcers
- abscess
- gangrene
- amputation
- diagnosis
- treatment
Septic arthritis
- in joints
- types
- mono- (90%) vs oligoarthritis (10%)
- iatrogenic septic arthritis
- cortisone injections
- often S. aureus
- S. penumoniae
- upper+lower airway infections
- meningitis
- arthritis
- N. meningitidis
- sepsis
- meningitis
- bacteriemia
- arthritis
- SOA-associated
- other, atypical arthritis
- Lyme arthritis
- incl. neurological signs
- diagnosis: serology (cf. Syphilis)
- reactive (post-infection) arthritis
In young children
- osteomyelitis + arthritis
- different vascularization in immature bone
- additional bacteria
- S. aureus
- S. pyogenes
- S. pneumoniae
- S. agalactiae: < 2m
- Kingella kingae: 6m - 2y
12 Invasive, zoonotic and vector-borne
Meningitis
Endocarditis
- bacteria colonize a heart valve
- group can break off and travel through the body
- fever comes and goes
- unpredictable symptoms
- higher risk patients
- artificial valves
- IV drug users
- HACEK organisms
- properties
- Gram negative
- slow growth
- incubate for 21 days instead of 2-4
- live in oropharynx
- cause 1.4% of endocarditis
- Haemophilus parainfluenzae
- Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans
- Cardiobacterium hominis
- Eikenella corrodens
- Kingella kingae
- cf. septic arthritis in young children
Septic thrombophlebitis
- definitions
- thrombus = blood clot
- embolus = piece of clot
- of cavernous sinusses
- associated with IV drug use
Post-partum complications
- chorioamnionitis
- remaining piece of placenta
Leptospirosis
- urine of rodents
- increasing due to climate change
Mycologie
- eukaryoten
- Onychomycosen
- Candida
- Aspergillus
- medicatie: imidazolen
Parasitologie
- eukaryoten
- symbiose
- commensalisme
- afhankelijkheid in 1 richting
- geen schade
- mutualisme
- win-win
- voorbeeld: darmflora
- parasitisme
- soorten
- obligate: kan enkel als parasiet overleven
- facultatieve
- complexe levenscyclus
- gastheer
- tussengastheer
- eindgastheer
- volwassen fase
- betere kans op overleving
- vector
- transmissiekanaal
- kan tussen- en eindgastheer zijn
- reservoir
- drager, vaak zonder ziek te worden
- taxonomie
- endoparasiet: binnenkant
- protozoa: eencellig
- sporozoa: niet-motiele eencelligen
- amoeben
- flagellaten
- metazoa: meercellig
- wormen
- nematoden = rondwormen
- platwormen
- Cestoden = lintwormen
- Trematoden = zuigwormen of botten
- ectoparasiet: buitenkant (op huid)
- ?
- trofozoieten: actief, voedend
- sporozoieten: infectieus (cf. sporen)
- (oo)cysten: cyste vorm van zygote
- behandeling: antiparasitaire middelen
- kleiner aantal
- toxischer voor mens (mede-eukaryoot)
- resistentie: beperkt probleem
- diagnose
- microscopie
- serologie
- enkel bij invasieve parasieten
- wormen: geen antistof resposne
- enkel bij eerste infectie
- zinloos in ontwikkelingslanden
- moleculaire detectie
- moeilijk
- stijgend aantal PCR testen
- antigen detectie (sneltesten)
- eosinofilie (richtinggevend)
- WBC: hoog aantal eosinofielen
- indeling per compartiment
- bloedparasieten
- GI parasieten
- weefselparasieten
- invasief -> serologie test
- ander
- genitaal
- urinair
- respiratoir
Protozoa (eencelligen)
Sporozoa
Malaria
- etymologie
- Plasmodium
- P. falciparum
- P. vivax
- Azie
- Oost-Afrika
- Zuid-Amerika
- P. ovale
- P. malariae
- bloedparasiet
- vooral in Sub-Sahara Afrika
- risico rond luchthavens
- levenscyclus
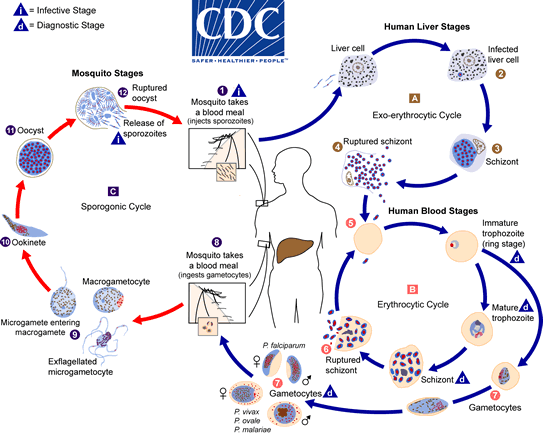
- vector: mug
- tussengastheer: mens
- mug injecteert sporozoioten in bloed
- asymptomatische fase in lever
- sporozoioten -> schizonten -> merozoieten
- P. vivax en P. ovale: ook sluimerende hypnozoieten
- risico op relapse jaren nadien
- symptomatisch fase in RBC
- merozoieten -> trofozoieten
- voeden met Hb en glucose
- kleverige RBC wand
- RBC hemolyse
- toxische metabolieten
- merozoieten -> gametocyten (M/V)
- mug zuigt gametocyten opnieuw op
- eindgastheer: mug
- gametocyten -> sporozoioten
- kliniek
- P. falciparum
- incubatie: 8-25d
- koorts, braken, diarree, hoofdpijn, spierpijn, ...
- nooit chronisch
- ernstige vorm
- microtromboses
- neurale impact
- nierfalen
- zwart water koorts (afbraak Hb)
- anemie
- hypoglycemie
- leverfalen
- andere P. soorten
- koorts in patronen
- soms chronisch
- langere incubatie
- minder ernstig
- immuniteit
- slachtoffers: vooral kinderen en zwangere vrouwen
- na meerdere infecties: eerder griep-achtig
- transient, verdwijnt na paar jaar
- hematologische afwijkingen: overlevingsvoordeel
- Sikkelcel anemie
- Thalassemie
- G6PD deficientie
- Duffy neg bloedgroep (?)
- diagnose
- microscopie van dikdruppel bloed
- P. falciparum
- "koptelefoon" in RBC
- banaanvormige gametocyten
- P. malariae
- bandvormige patronen in RBC
- sneltest (antigen)
- hoge sensitiviteit
- enkel voor P. falciparum
- serologie (antistoffen)
- beperkt gebruikt - enkel referentielabo's
- preventie
- bed nets = klamboe
- profylaxe
- vaccin
- enkel voor locals, niet voor reizigers
- RTS,S vaccin
- lage effectiviteit
- boosters nodig
- R21/matrix M vaccin
- behandeling
- Chloroquine
- resistentie bij P. falciparum
- Artemisine-combinatie therapie (ACT)
- primaquine tegen hypnozoieten bij P. vivax/ovale
Toxoplasmose
- weefselparasiet
- wereldwijd
- milde ziekte
- gevaar bij zwangerschap: moeder -> foetus
- vroeger = ernstiger
- klassieke triade (zeldzaam)
- chorioretinitis
- hydrocephalus
- intracraniele calcificaties
- lifecycle
- tussengastheer: varia
- oocyste -> tachyzoiet -> bradyzoiet
- eindgastheer: kat
- transmissie
- ingestie
- onvoldoende doorbakken vlees
- oocysten uit omgeving (moestuin, ...)
- orgaantransplantatie
- kliniek
- vaak asymptomatisch
- heropflakkering bij verzwakt immuunsysteem (HIV)
- diagnose
- serologie (IgG, IgM)
- IgG aviditeit (affiniteit voor antigen)
- laag -> recente infectie
- hoog -> langer geleden (> 4m)
- PCR
- bloed
- vruchtwater
- CSF
- voorkamervocht oog
Cryptosporidium
- GI parasiet
- C. parvum
- C. hominis
- enteritis
- transmissie
- lifecycle
- oocysten
- sporozoieten
- trofozoieten
- merozoieten
- gametocyten
- oocysten
- diagnose
- microscopie met speciale kleuring
- PCR
- antigen
- behandeling
- bij gezonde mensen: geen
- HIV: HAART tegen HIV zelf
Amoeben - Entamoeba histolytica
- GI- en weefselparasiet
- transmissie: feco-oraal
- invasieve enteritis
- leverabces
- meestal eerder microbieel
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- polymicrobieel
- of andere parasieten
- behandeling: AB > metronidazole (7-10d)
- standaard bij elk leverabces
- diagnostiek
- serologie
- faeces
- leveraspiraat
Flagellaten
Giardia lamblia
- GI parasiet
- vooral bij slechte hygiene
- transmissie: feco-oraal
- milde symptomen
- diagnostiek
- microscopie
- antigen op faeces
- PCR
- behandeling
Trichomonas vaginalis
- genitaal
- SOA
- incubatie: 5-28 dagen
- symptomen
- vooral bij vrouwen
- witverlies, geur, jeuk
- urethritis
- prostatitis
- diagnose
- behandeling
Trypanosoma brucei
- slaapziekte
- bloedparasiet
- lifecycle
- vector: tseetsee vlieg (Glossina sp.)
- reservoir: vee
- tussengastheer: mens
- eindgastheer: tseetsee vlieg
- types
- gambiense (97%)
- C-/W-Afrika
- vector: Glossina palpalis
- chronisch
- rhodesiense (3%)
- O-/Z-Afrika
- vector: Glossina morsitans
- symptomen
- eerste fase
- tweede fase
- gambiense veel trager dan rhodesiense
- zware neurologische symptomen
- mortaliteit (zonder medicatie): 100%
- diagnose
- behandeling
- afhankelijk per fase en per type
- zeer toxisch
Platwormen
Trematoden (zuigwormen of botten)
- GI parasiet
- Schistosomiase
- zwemmen in zoet water in tropisch gebied
- Lake Malawi
- recent ook al in Corsica
- lifecycle
- tussengastheer: zoetwaterslak
- eindgastheer: mens?
- huid -> bloed -> veneuze plexus (lever/blaas) -> stoelgang/urine
- milde symptomen
- swimmer's itch
- vooral ontsteking rond verdwaalde eitjes
- diagnostiek
Cestoden (lintwormen)
- GI parasiet
- Taenia infecties – cysticercosis
- 4-10m
- transmissie: weefselcystes in voeding
- lifecycle
- tussengastheer: koe/varken/mens
- larven -> weefsel -> cyste
- eindgastheer: mens
- types
- Taenia saginata = runderlintworm
- Taenia solium = varkenslintworm
- uitgeroeid in Belgie
- enkel hier mens als tussengastheer
- symptomen
- mild
- bij tussengastheer
- cysticercus / cysticerose
- bij eindgastheer
- diagnose
- microscopie faeces
- eieren
- stukjes worm (proglottides)
Nematoden (rondwormen)
Enterobius vermicularis (aarsworm)
- ook in Belgie
- transmissie: feco-oraal
- geen tussengastheer nodig
- symptomen
- jeuk door eitjes aan anusrand
- onder vingernagels -> mond -> auto-infectie
- diagnose: tape test
- plakband rond anus
- plakband in petri schaal
- bekijk onder microscoop
- behandeling
Ascaris lumbricoides (spoelworm)
- minder belangrijk
- 1B besmettingen
- transmissie: feco-oraal
- lifecycle
- tussengastheer: mens
- eindgastheer: ook mens
- larven naar long
- hoesten: long -> dunne darm
- milde symptomen
- eitjes moeten rijpen in omgeving
Strongyloides stercoralis
- minder belangrijk
- iets ernstiger
- auto-infectie
- blote voeten -> huid -> bloed -> longen -> GI
- diagnose


