Bloedsomloop - Fysiologie
- primaire doodsoorzaak
- mannen: ischemisch hartleiden
- vrouwen: dementie, dan cardiovasculaire problemen
- secundair (US, 2021): kanker
20 Microcirculatie
Anatomy
- metarteriolen: bypass from artery to vein
- endothelial connections
- between
- cleft: 10-15nm
- gap: 100-1000nm
- within
- fenestration: 50-80nm
- between
- leakiness (low -> high)
- continuous capillary
- most common
- clefts
- brain: BBB, tight junctions
- fenestrated capillary
- in small intestine
- fenestrations
- sinusoidal capillary
- in liver
- large fenestrations
- gaps
- continuous capillary
Exchange
- gasses
- O2
- 98% in HbO2
- 2% dissolved
- CO2
- 90% in HCO3-
- 5% dissolved
- transcellular diffusion
- Krogh model / Fick
- : flow
- demand
- delivery
- extraction ratio
- highest in heart and active skeletal muscle
- artery -> vein
- "gemengd veneus bloed"
- saturation SvO2 = 70%
- t.h.v. pulmonary artery
- 37% (sinus coronarius) tot 81% (nier) op andere plaatsen
- (ml/dl)
- : 20 ml/dl -> 15 ml/dl
- : 95 mmHg -> 40 mmHg
- : 97% -> 75%
- at rest: 3.5 ml/min/kg
- : 48 ml/dl -> 52 ml/dl
- : 40 mmHg -> 46 mmHg
- at rest: 2.8 ml/min/kg
- respiratory quotient
- "gemengd veneus bloed"
- O2
- small solubles
- glucose, ureum, Na+, Cl-, K+, hormones, ...
- paracellular diffusion
- Fick
-
- : capillary
- : interstitial fluid
- flux [mol/cm2 s]
- permeability coefficient [cm/s]
- higher for smaller compounds
- negative << neutral << positive
- diffusion coefficient [cm2/s]
- wall thickness [cm]
- concentration
-
- macromolecules
- paracellular diffusion via clefts: limited
- transcytosis
- slow
- "sieving": higher for smaller molecules
- breakdown of certain proteins, e.g., ferritin
- minimal transport in BBB
- water
- transcellular via aquaporin1 (AQP1)
- paracellular
- convection (Starling forces)
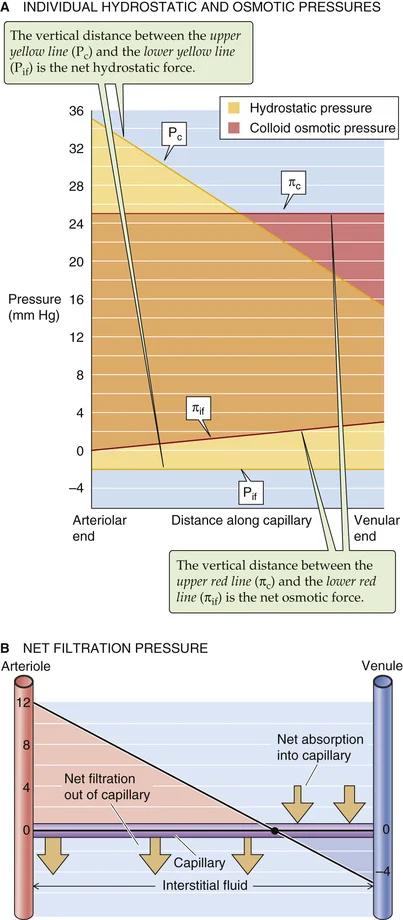
- Starling hypothesis
- c: capillary
- if: interstitial fluid
- : volume flux
- : hydrolic conductivity
- rest: net filtration pressure
- hydrostatic pressure
-
- arteriole:
- venule:
- varies
-
- exceptions: kidney (+10), brain, lungs (varies with respiration)
-
- colloid osmotic (=oncotic) pressure
- due to plasma proteins (7 g/dl, mostly albumine)
-
- on average
- varies
-
: reflection coefficient
- usually
- hydrostatic pressure
- : flow across wall
- : functional surface area
-
: filtration
- : ultrafiltration
- : absorption
- Starling hypothesis
Lymph
- driver:
- effect depends on compliance of surrounding tissue
- "oedema begets more oedema"
- effect depends on compliance of surrounding tissue
- also transports proteins
- unidirectional valves
- oedema
- pleura
- ascites: peritoneal
- pulmonary oedema
- hypoproteinemia: low albumine
- low
- nephrotic syndrome
Regulation
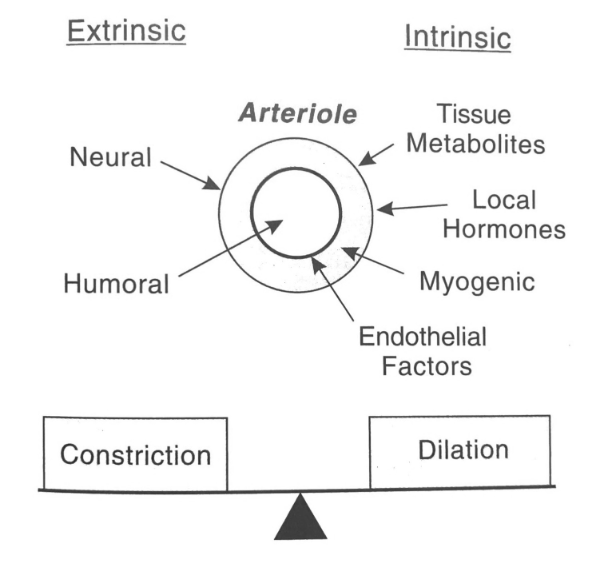
- regulation via
- arterioles
- precapillary sphincters
-
constriction
- affects SVR
-
dilation
- affects organ blood flow + O2 delivery
- ATP/ADP
- adenosine
- histamine
- VIP
- ACh via endothelium (NO)
- extrinsinc control
- neural (autonomous)
- vasodilation
- parasympathetic
- n. vagus (X)
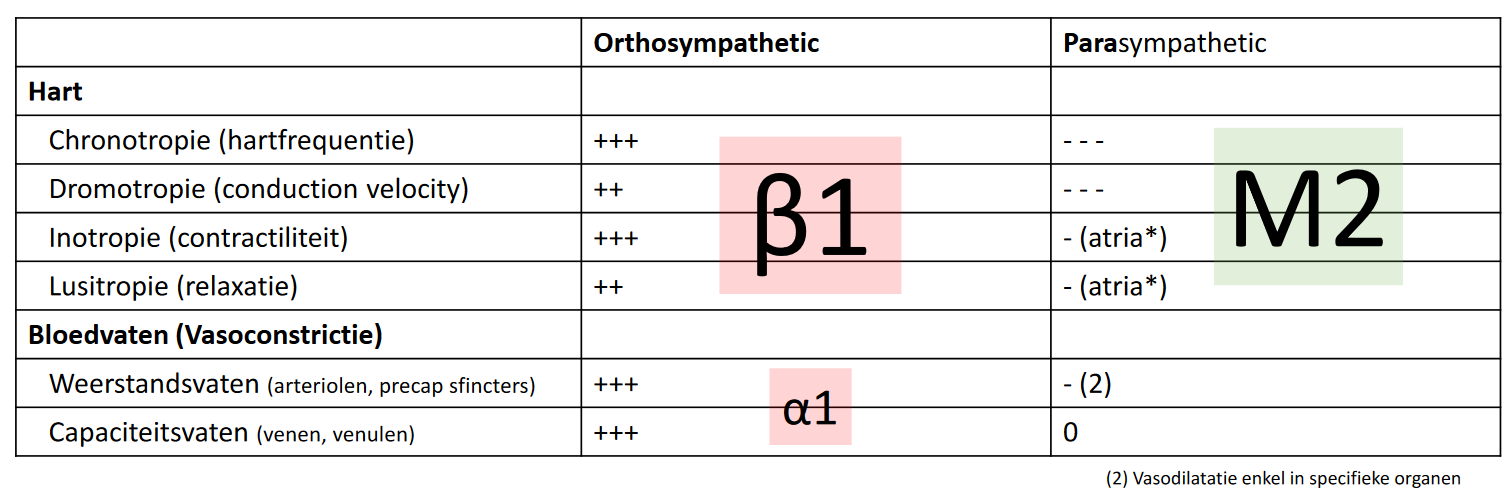
- ACh (M2 receptor)
- orthosympathetic
- adrenaline ( receptor): muscles + coronaries
- parasympathetic
- vasoconstrinction
- orthosympathetic
- postgangionic
- noradrenaline ( receptor)
- orthosympathetic
- vasodilation
- humoral (i.e., blood itself)
- global effect, not local
- vasoconstrinction
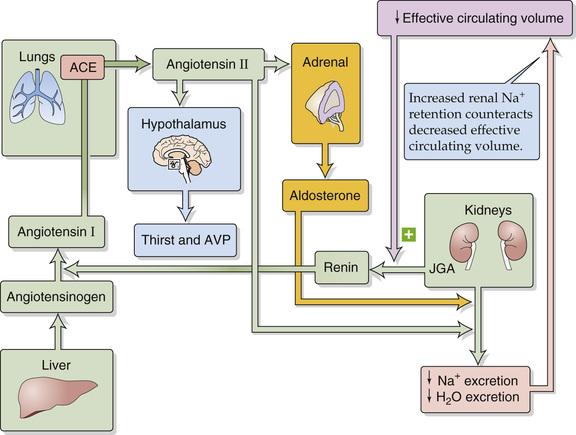
- renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system (RAAS)
- angiotensin = ANG @ liver
- kidney @ renine (during hypotension)
- ANG -> ANG I
- angiotensine converting enzyme (ACE)
- ANG I -> ANG II
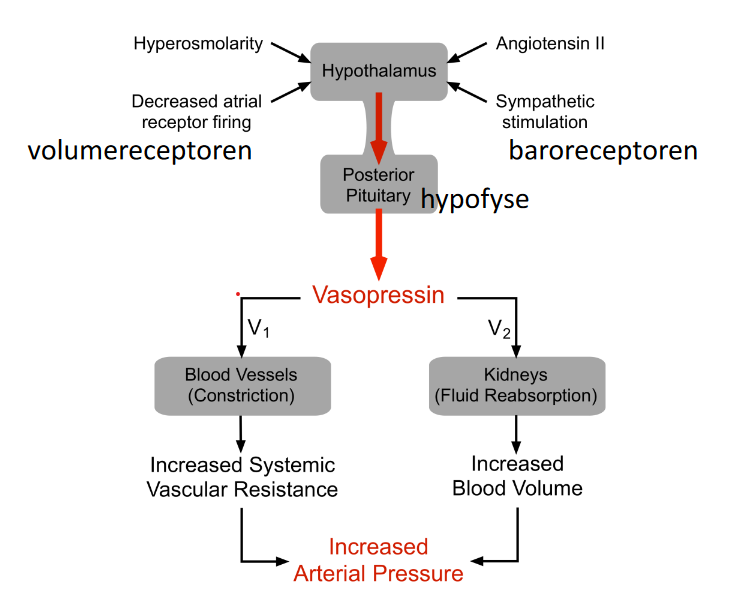
- arginine vasopressine (AVP) = ADH
- ANG II (and others)
- hypothalamus
- posterior pituitary
- AVP
- effect 1: vasoconstriction
- effect 2: fluid reabsorption @ kidney
- renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system (RAAS)
- intrinsic control
- local hormones + tissue metabolites
- paracrine
- histamine
- bradykinin
- prostaglandines
- PO2 drop
- systemic: dilation
- pulmonary: constriction
- vasodilator substances (K+, H+, CO2, PO4-, lactate, adenosine)
- paracrine
- endothelial factors
- endothelial cells
- detect shear stress
- release NO
- causes vasodilation
- i.e., erections
- causes vasodilation
- other triggers
- hormones (endo / paracrine)
- hypoxia
- endothelial cells
- myogenic autoregulation
- goal: stabilize when changes
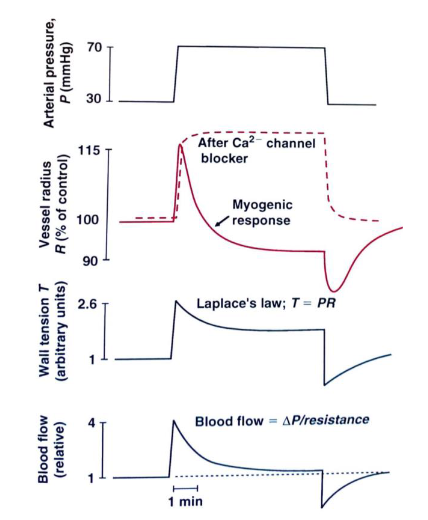
- special circulations (see later)
- strong autoregulation: brains, heart, kidneys
- weak/no autoregulation: skin
- angiogenesis
- promotors
- inhibitors

21 Elektrofysiologie en ECG
Elektrofysiologie
Actiepotentiaal
- membraanpotentiaal: -70mV (varies per tissue)
- in rust
- binnen: -
- buiten: +
- in rust
- ionen
- K+, vooral binnen
- repolarisatie
- Ca2+, vooral buiten
- instroom -> depolarisatie
- in SA en AV node
- slow response AP
- 3 fasen
- 0 trage depolarisatie
- geen Na+ stroom
- 3 repolarisatie
- 4 pacemaker
-
?: funny current
- cation (Na+, K+) kanaal
-
?: funny current
- 0 trage depolarisatie
- Na+, vooral buiten
- instroom -> depolarisatie
- in spierweefsel + Purkinje
- fast response AP
- 5 fasen
- 0 snelle depolarisatie
- binnen -
- Na+ instroom
- 1 snelle repolarisatie
- binnen +
- K+ uitstroom
- 2 plateau
- binnen +
- Ca2+ in
- K+ uit
- 3 repolarisatie
- binnen -
- K+ uit (chemische gradient)
- AP duur
- subepicard < subendocard < midmyocard
- RV < LV
- basis < apex
- dus: basis -> apex + epicard -> endocard
- 4 diastole
- binnen -
- 0 snelle depolarisatie
- 5 fasen
- fast response AP
- K+, vooral binnen
- kanalen
- NCX1: 3Na+ in vs 2Ca2+ uit
- passief
- 2K+ in vs 3Na+ buiten
- ATP
- H+ in vs Ca2+ uit
- ATP
- gap junctions
- connexine 43
- NCX1: 3Na+ in vs 2Ca2+ uit
- conductantie
- Nernst:
- refractaire periodes (RP)
- ARP: absolute RP
- geen depolarisatie
- ERP: effectieve RP
- geen voortgeleiding
- RRP: relative RP
- sterkere stimulus nodig voor depolarisatie
- ARP: absolute RP
Conductie
- flow
- SA
- atrium
- AV
- His bundle
- Purkinje
- right
- left
- anterosuperior
- posteroinferior
- ventrikel
- geleidingssnelheid = dromotropie
- ~ diameter
- AV (klein) -> traag
- Purkinje (groot) -> snel
- hogere depolarisatie -> sneller
- stimulatie
- sympatisch: sneller
- parasympatisch: trager
- varia
- kenmerken celmembraan
- kenmerken gap junctions
- kenmerken cytoplasma
- ~ diameter
- linker bundeltakblok
Modulatie
- contractiliteit = inotropie
- frequentie SA = chronotropie
- waarom
- hoe
- decreased rate of depolarization -> trager
- negative shift in max diastolic -> trager
- positive shift in threshold -> trager
- stimulatie
- sympatisch: sneller
- hypotensie
- fight or flight
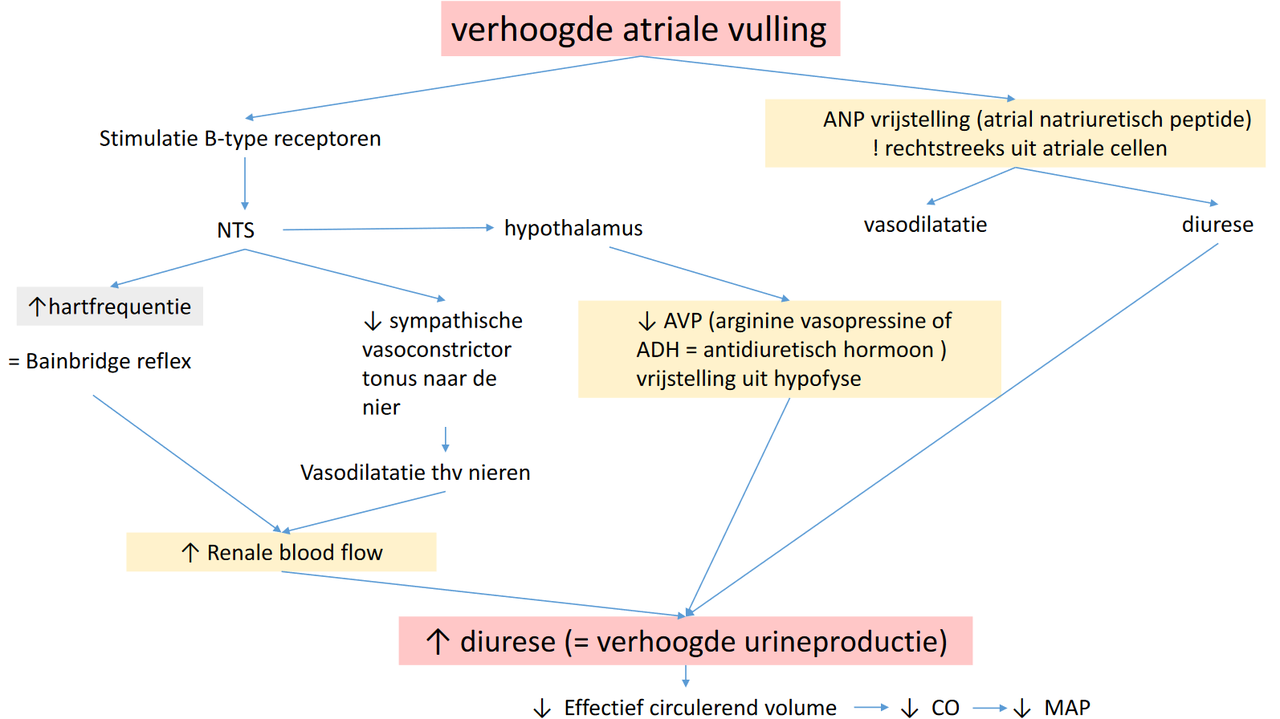
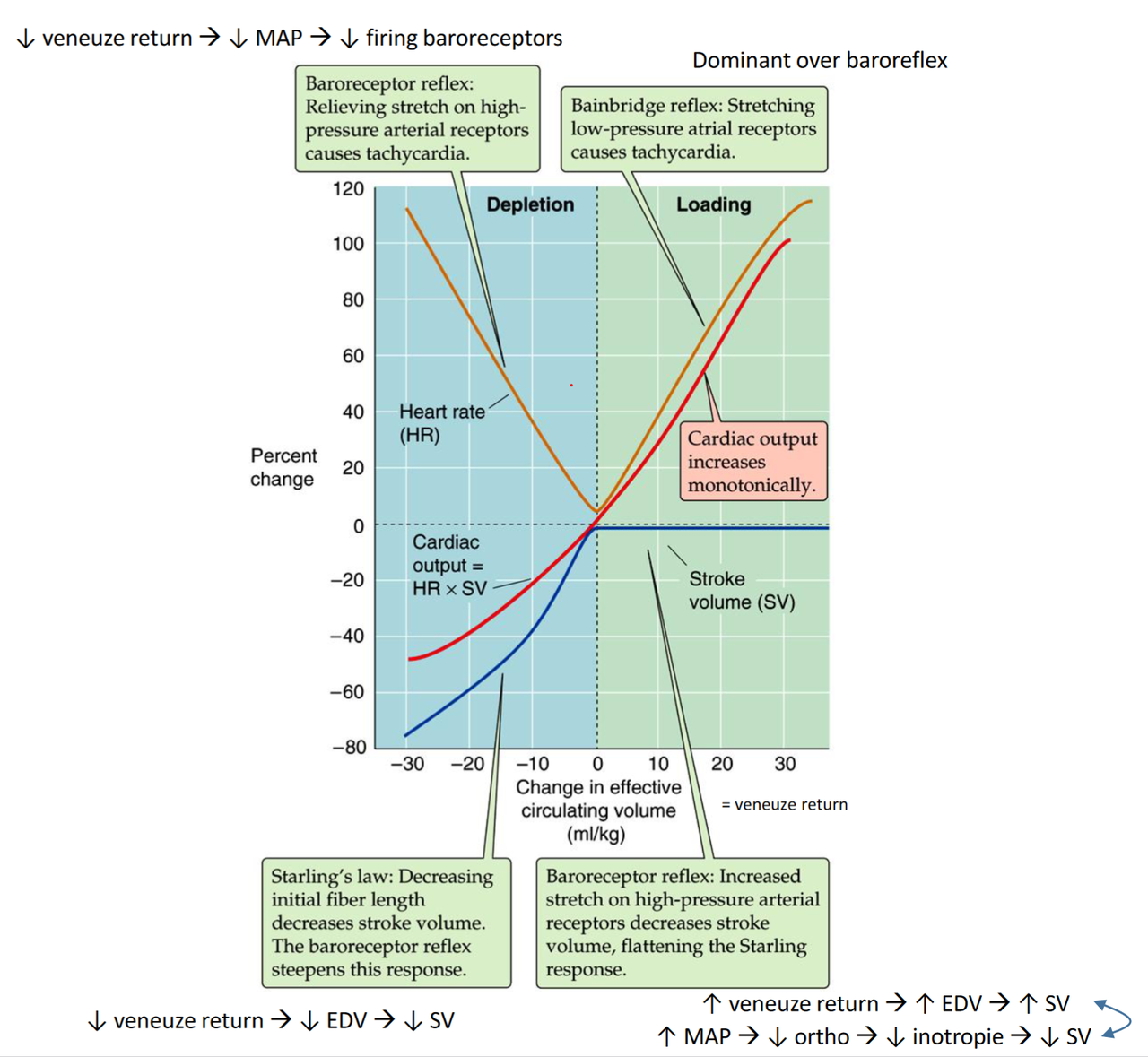
- Bainbridge reflex
- parasympatisch (n. vagus): trager
- baroreflex
- sympatisch: sneller
- catecholamines @ bijnier: sneller
- waarom
- frequentie
- intrinsiek: 100-110 bpm
- normaal: 60-100 bpm
- : brady aritmie
- : tachy aritmie
- max: 220 bpm - leeftijd
ECG

- meet spanning buiten cel
- in rust: +
- depolarisatie: -
- nomenclature
- deflectie
- iso-elektrisch lijnstuk: vlak
- hoofdletters
- mm: X
- mm: x
- P wave
- QRS complex
- Q, R, S, wave
- T wave
- segment
- isoelektrisch
- ST
- tot begin T golf
- T golf kan er niet bij, want dan niet meer isoelektrisch
- interval
- RR
- PR
- tot begin QRS (dus eigenlijk PQ?)
- QT
- tot einde T golf (cf. ST)
- QRS
- hartvector
- voortplantingsrichting van depolarisatie
- van min naar plus (buiten cellen)
- voortplantingsrichting van depolarisatie
- afleidingas
- as door 2 elektroden (min naar plus)
- projectie van op
- naar plus: positief
- naar min: negatief
- deflectie
- afleidingen
- RL: zwart (aarding)
- LL: groen
- RA: rood
- LA: geel ("zon boven groene gras")
- van min naar plus
- frontaal
- 3 standaard/bipolair (driehoek Einthoven)
- lead I: RA -> LA
- lateral
- lead II: RA -> LL
- inferior
- lead III: LA -> LL
- inferior
- I + III = II
- lead I: RA -> LA
- 3 augmented/unipolair (Goldberger)
- aVR: -> RA
- N/A
- aVL: -> LA
- lateral
- aVF: -> LL
- inferior
- aVR: -> RA
- 3 standaard/bipolair (driehoek Einthoven)
- horizontaal / transversaal
- 6 precordiale afleidingen (t.o.v. sterpunt Wilson)
- CT: central terminal
- V1
- 4th intercostal space
- right of sternum
- septal
- V2
- 4th intercostal space
- left of sternum
- septal
- V3
- between V2 and V4
- anterior
- V4
- 5th intercostal space
- midclavicular line
- anterior
- V5
- 5th intercostal space
- between V4 and V6 (anterior axillary line)
- lateral
- V6
- 5th intercostal space
- midaxillary line
- lateral
- extra
- V3R - V6R
- V7
- V8
- 6 precordiale afleidingen (t.o.v. sterpunt Wilson)
- main/mean? heart axis o.b.v. I+aVF
- normaal: -30 tot 90 graden (kwadrant IV+)
- LAD: -30 tot -90 (deel kwadrant I)
- RAD: 90 tot 180 (kwadrant III)
- EAD: 180 tot -90 (kwadrant II)
- deflection per lead during QRS
- pos / neg / equiphasic
- Lead I en aVF: loodrecht assenstelsel
- pos/pos = 2x thumps up = normaal
| aVF: pos | aVF: neg | |
|---|---|---|
| I: pos | normaal | LAD |
| I: neg | RAD | inderterminate |
- schaal
- lengte:
- 25 mm/s -> 1 mm = 40 ms
- soms ook 50-200 mm/s
- 25 mm/s -> 1 mm = 40 ms
- hoogte
- 1 mm = 0.1 mV
- kleine vierkantjes: 1x1 mm2 = 40 ms x 0.1 mV
- grote vierkanten: 5x5 mm2 = 200 ms x 0.5 mV
- 5 grote vierkanten: 25x25 m22 = 1s x 2.5 mV
- lengte:
- kalibratie
- 1 mV = 10 mm
- 200 ms = 5 mm -> 25 mm/s
- interpretatie
- RR interval (ms)
- 1 (groot) vierkant / 200 ms = 300 vierkanten / min
- hartfrequentie (bpm)
- enkel bij regelmatig ritme
- P wave
- depolarisatie atria
- II: positief
- V1: bifasisch (op/neer)
- PR interval
- 120 - 200 ms
- P wave + AV + His + purkinje
- QRS complex
- depolarisatie ventrikels
- < 100 ms
- : initial
-
: main
- links >> rechts
- : terminal
- endocard -> epicard
- endo: begint eerst, laatst gedaan
- T wave
- repolarisatie ventrikels
- epicard -> endocard
- QT interval
- correctie voor HR
-
- 60 bpm
-
- geen leerstof
-
- long QT syndrome (LQTS)
- QT < 420: onwaarschijnlijk
- QT > 460: verlengd
- quick check: normaal als klaar voor 1/2 RR interval
- factoren
- watervat analogie
- instroom/depolarisatie (Na+, Ca2+)
- aantal kanalen
- doorlaatbaarheid
- uitstroom/repolarisatie (K+)
- depolarisatie = hoger waterniveau
- repolarisatie = terug naar evenwichtsniveau
- instroom/depolarisatie (Na+, Ca2+)
- watervat analogie
- correctie voor HR
- RR interval (ms)
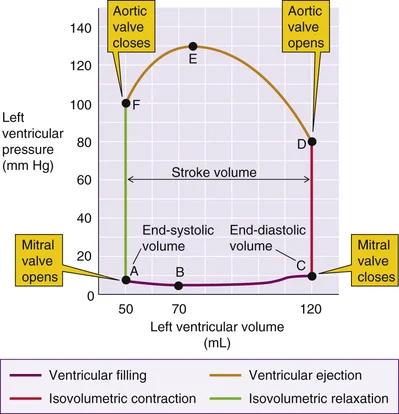
- fasen
- atrial systole
- isovolumetric contraction
- rapid ejection
- decreased ejection
- isovolumetric relaxation
- rapid ventricular filling
- decreased ventricular filling (diastasis)
Ritmestoornissen
- brady: < 60 bpm
- tachy: > 100 bpm
- abnormale prikkelvorming
- automaticiteit
- verlaagd
- para
- medicatie (beta blocker, Ca2+ blocker)
- verhoogd
- ectopisch
- bij ischemie
- Na+ kanalen inactief
- depolarisatie
- bij ischemie
- verlaagd
- getriggerde activiteit
- ectopisch
- early afterdepolarization (EAD)
- binnen vorige AP
- bij verlenging van AP
- bradycardia
- hypokaliemie
- long QT
- delayed afterdepolarization (DAD)
- na repolarisatie
- Ca2+ overload
- bij tachy
- early afterdepolarization (EAD)
- ectopisch
- automaticiteit
- abnormale prikkelgeleiding
- vertraging / blok
- oorzaken
- intrinsiek (anatomie)
- fibrose
- ischemie
- extrinsiek (functioneel)
- para
- medicatie
- intrinsiek (anatomie)
- soorten
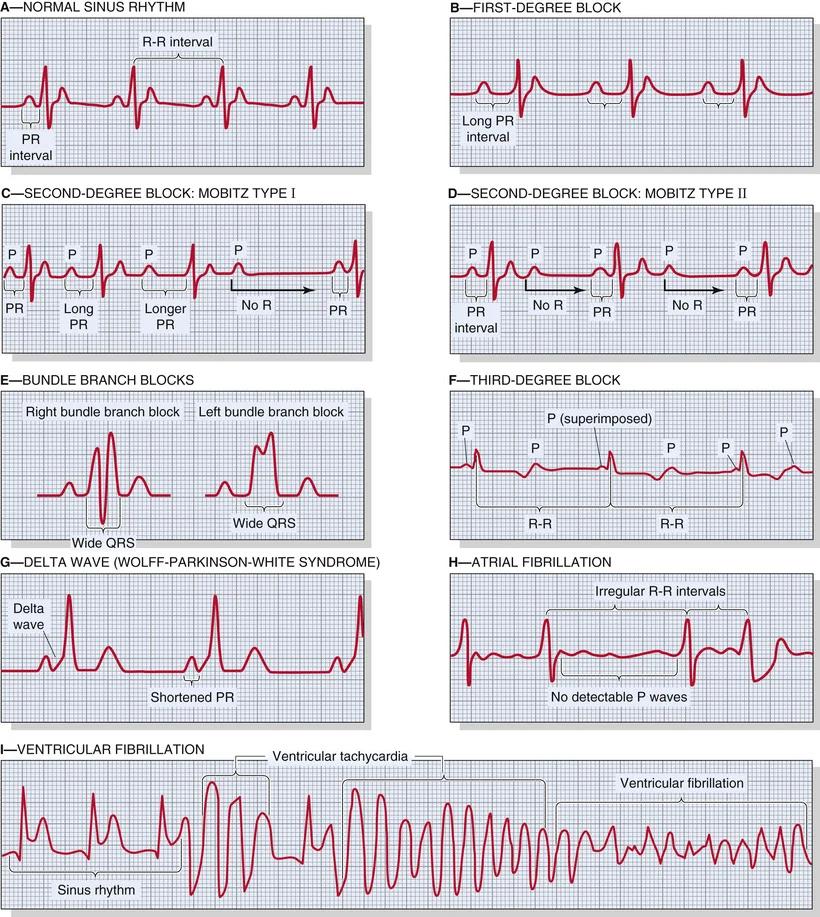
- AV blok
- graad 1
- long PR (> 200ms)
- graad 2
- Mobitz type I
- P langer en langer
- tot geen QRS meer
- Mobitz type II
- P blijft even lang
- soms geen QRS
- Mobitz type I
- graad 3
- geen verband meer tussen P en QRS
- graad 1
- bundeltakblok
- links of rechts
- breed QRS (> 120ms)
- AV blok
- oorzaken
- re-entry
- rondjes draaien
- voorwaarden
- unidirectionele blok (cf. diode)
- zone van vertraagde conductie
- korte refractaire periode
- wavelength = refractaire periode x conductiesnelheid
- fibrillatie
- chaos
- voorkamerfibrillatie (VKF)
- geen P golven
- onregelmatig RR interval
- vertrikelfibrillatie (VF)
- levensbedreigend
- chaos ipv QRS complex
- vertraging / blok
- ischemie
- O2 vraag > aanbod
- hypoxie: minder O2
- anoxie: geen O2 meer
- acuut coronair syndroom
- diagnose in < 10min nodig
- anders myocardinfarct
- necrose (irreversibel)
- QS golf zonder R
- necrose (irreversibel)
- anders myocardinfarct
- obstructie
- volledig
- 60 min behandeltijd
- stent
- transmuraal
- epicardiale zijde meest gevoelig
- gedeeltelijk
- 24u tijd
- eerst medicatie proberen
- endocardiale zijde meest gevoelig
- volledig
- methode 1: check troponine in bloed
- indicator van necrose
- duurt te lang
- methode 2: ECG
- check V5
- ST segment elevation
- = ST-elevation mycardial infarction (STEMI)
- bij volledige obstructie
- ST segment depression
- = non ST-elevation mycardial infarction (NSTEMI)
- bij gedeeltelijke obstructie
- diagnose in < 10min nodig
- cellulaire gevolgen in cardiomyocyt
- O2 down -> ATP down
- meer extracellulair K+
- meer intracellulair Ca2+
- anaerobe ademhaling -> acidose
- ECG effect
- rustpotentiaal minder negatief
- tragere depolarisatie
- beperktere depolarisatie
- snellere repolarisatie
- ischemische diastolische vector
- ischemische systolische vector
- wijst naar zone O2 tekort
- partieel: naar binnen
- volledig: naar buiten
- wijst naar zone O2 tekort
- O2 vraag > aanbod
Werkzitting ECG
- hartas bepalen
- methode 1: lead I + lead aVF
- hartfrequentie bepalen
- regelmatig
- 300 / aantal grote blokken in 1 RR interval
- onregelmatig
- QRS complexen per 5s x 12
- regelmatig
Werkzitting ritme
22 Pomp
Hartcyclus
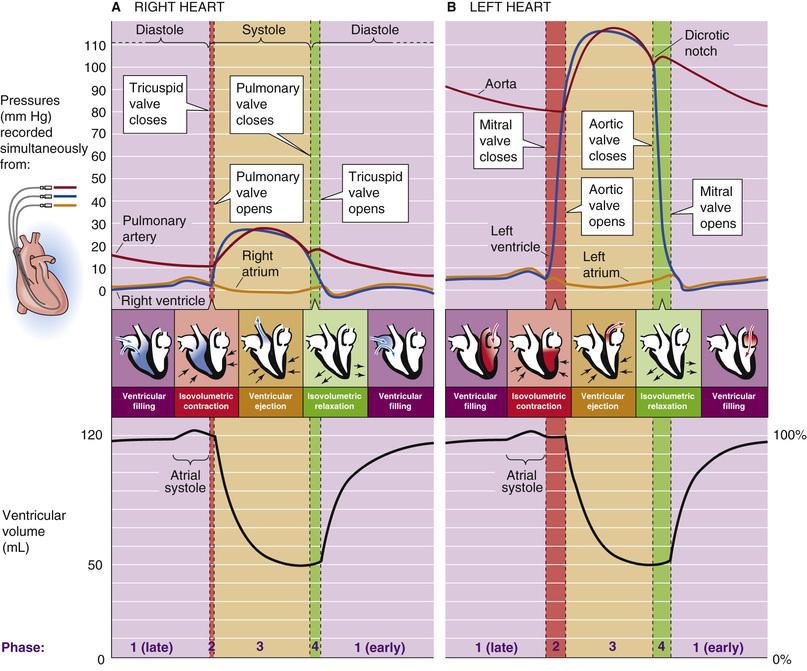
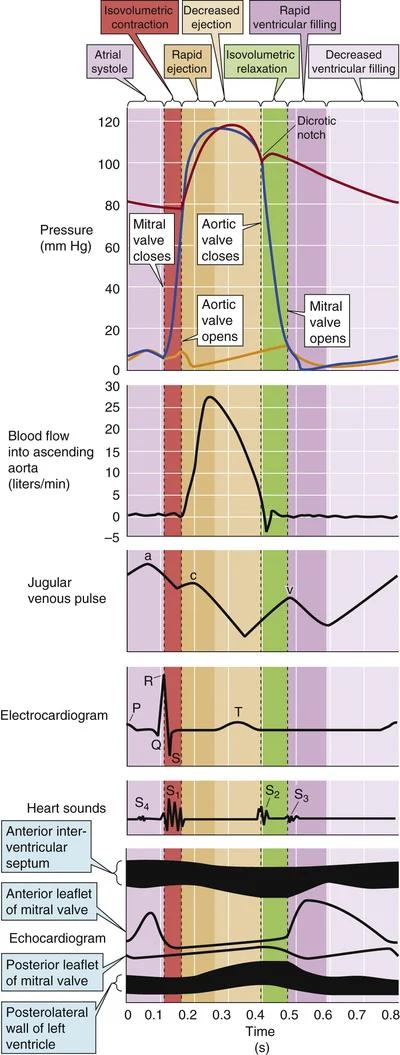

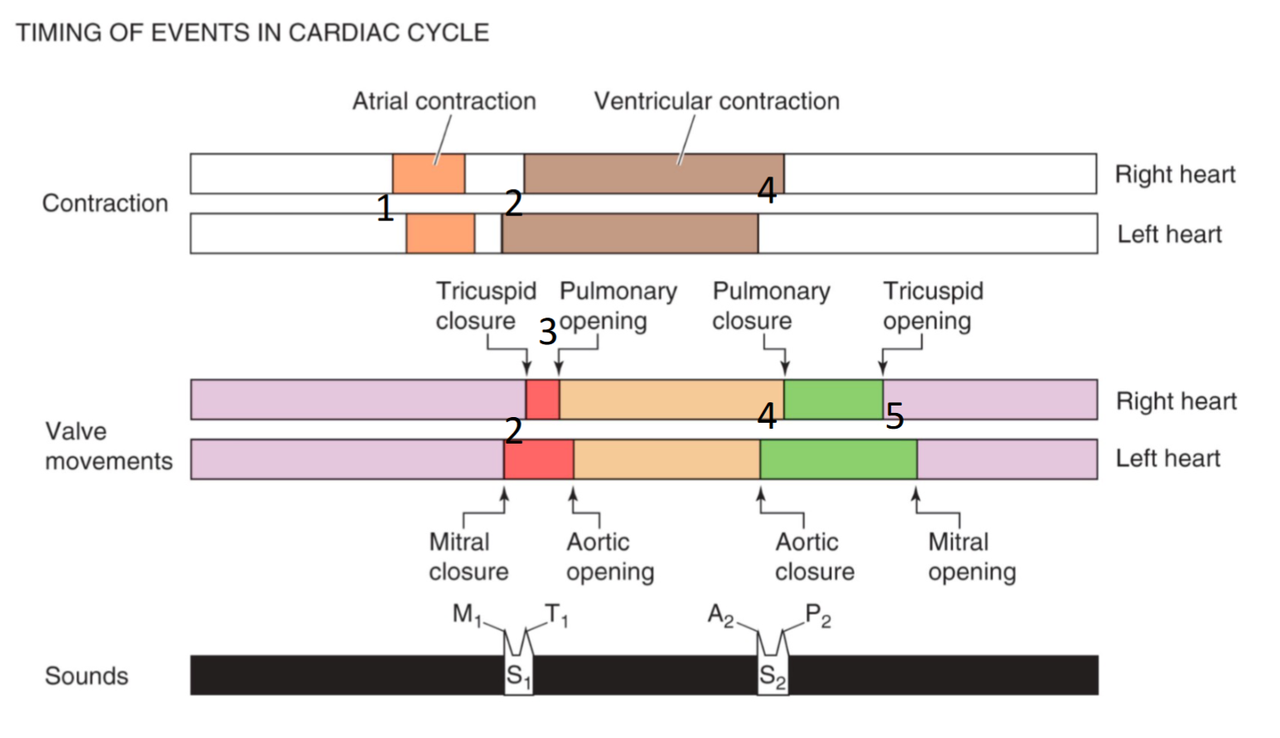
- hoger ritme: vooral diastole tijd neemt af
- 4 fasen
- 1 diastole: open AV valves
- vroeg
- snelle ventriculaire vulling
- laat
- vertraagde V vulling = diastase
- A contractie
- P golf
- vroeg
- 2 systole: close AV valves
- isovolumetrische contractie
- harttoon S1
- QRS complex
- 3 systole: open semilunar valves
- druk aorta druk LV
- als druk lager ligt: mogelijk klepstenose die veel weerstand geeft
- "systolische souffle" (zie onder)
- als druk lager ligt: mogelijk klepstenose die veel weerstand geeft
- snelle ejectie
- vertraagde ejectie
- druk aorta > druk LV
- maar bloed blijft kort verder stromen door inertie
- T golf
- druk aorta druk LV
- 4 diastole: close semilunar valves
- isovolumetrische relaxatie
- S2
- 1 diastole: open AV valves
- 4 harttonen
- S1
- lub
- sluiting AV kleppen
- subtiel: eerst mitralis, dan tricuspid
- S2
- dub
- sluiting semilunaris kleppen
- splitst bij inspiratie
- drukverlaging
- betere vulling RV
- tragere ejectie in a. pulmonalis
- dus eerst aortaklep dicht
- dan pulmonaalklep dicht
- OS
- opening stenotische mitralisklep
- S3
- vroege diastole: "galop"
- normaal enkel bij jongeren
- anders diastolische dysfunctie
- S4
- atriale contractie: "galop"
- diastolische dysfunctie
- S1
- hartgeruisen (souffle)
- tussen S1-S2: systolisch
- aorta stenosis
- mitraal regurgitatie
- tussen S2-S1: diastolisch
- aorta regurgitatie
- mitraal stenosis
- tussen S1-S2: systolisch
- rechts vs links
- conceptueel gelijk
- volume: R == L
- druk: R << L
- timing
- RA -> LA
- LV -> RV
- drukgolven
- arteries
- compliantie
- ouder -> stijver
- ziekte -> vervorming aorta -> eerdere reflectiepunten
- reflecties
- compliantie
- capillairen
- geen pulsatie
- venen
- niet: voortzetting drukgolf arteries
- retrograde actie hart
- ademhaling
- inademen
- thorax
- lagere druk
- meer veneuze return
- lagere druk in v. jugularis
- abdomen
- hogere druk
- minder veneuze return
- hogere druk in v. femoralis
- thorax
- inademen
- skeletspieren
- arteries
Dynamica
Morfologie
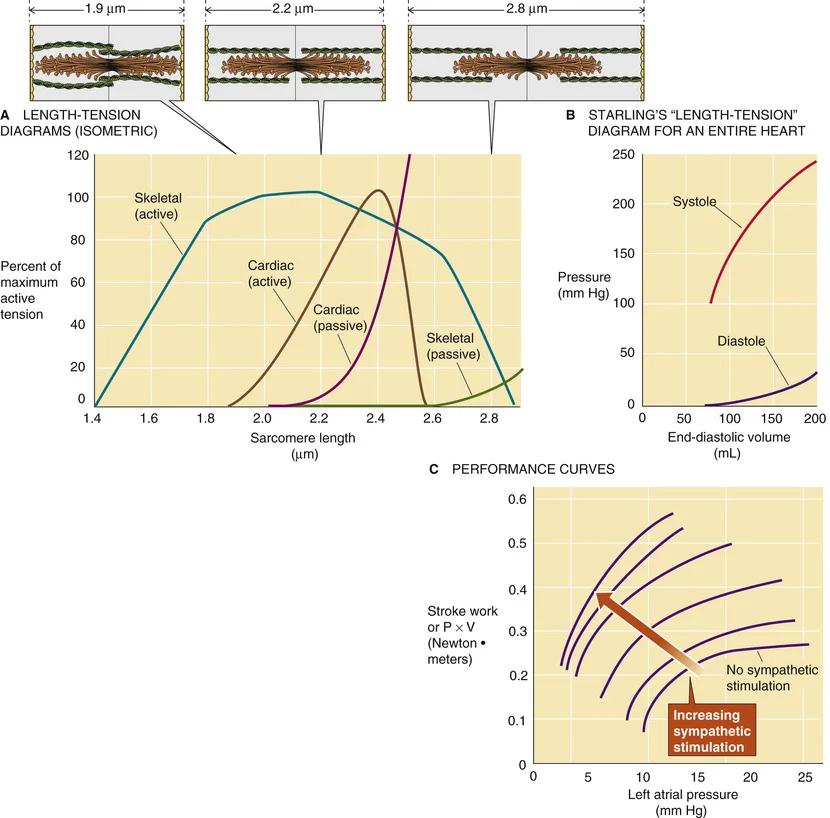
- length-tension diagram van sacromeer
- actief vs passief
- skelet vs myocard
- actief myocard
- piek, kleine spreiding
- 2.2 um length -> 60% tension
- 2.4 um length -> 100% tension
- wet van Frank-Starling
- vertaling
- sacromeer (micro) -> hart (macro)
- actief -> systole
- passief -> diastole
- length -> volume (LVEDV), LVEDP, LAP
- tension -> SBP, SV, CO, BP
- groter einddiastolisch volume (EDV) -> groter SV
- vertaling
Evaluatie pompfunctie
- cardic index
- < 2.2 l/min/m2 -> shock
- EDV = 120 ml
- ESV = 50 ml
- SV = EDV - ESV = 70 ml
- ejectiefractie
- normaal >= 55%
- druk (mmHg)
- aorta: 95
- PA: 15
- sys capillairen: 25
- pulm capillairen: 10
- contractiliteit ~ dP/dt
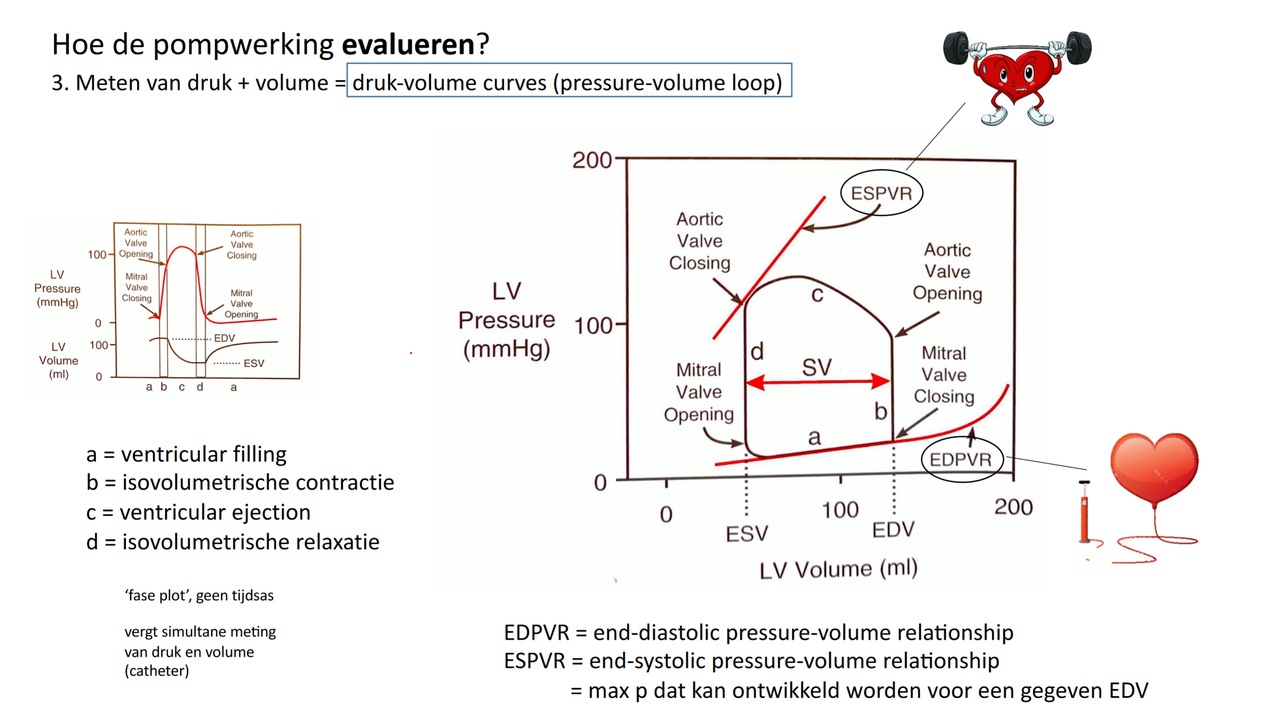
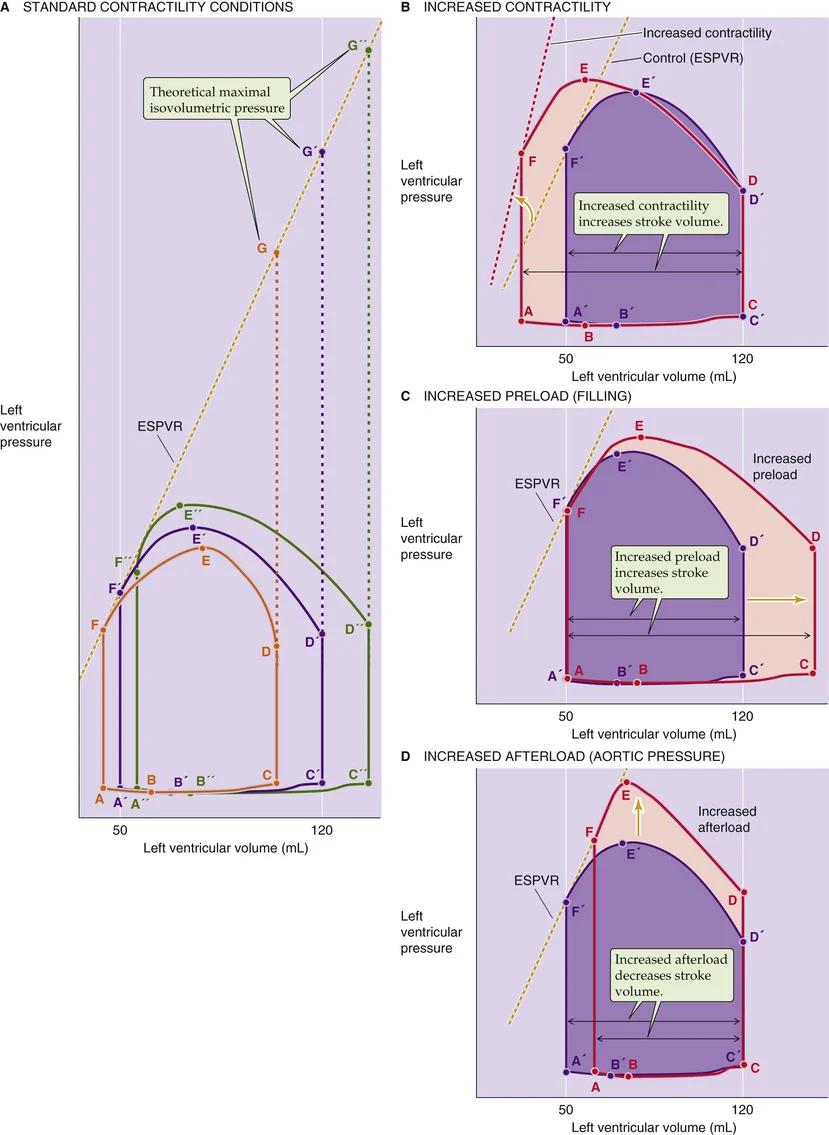
- druk-volume (PV) curve/loop
- cf. Wiggers diagram
- 4 fases
- diameter = SV
- energie
- extern + extern + intern
- extern: 3-10%
- intern
- drukopbouw zonder beweging
- Laplace
- extern + extern + intern
- flowsnelheden
- echo
- doppler: v(t) -> -> x -> V=xA -> SV
- stress-strain
- Fick
- SvO2 drop -> CO drop
- thermodilutie
- koud water in
- op later punt detecteren -> AUC
- CO = Q_in / AUC
- echo
Regulatie
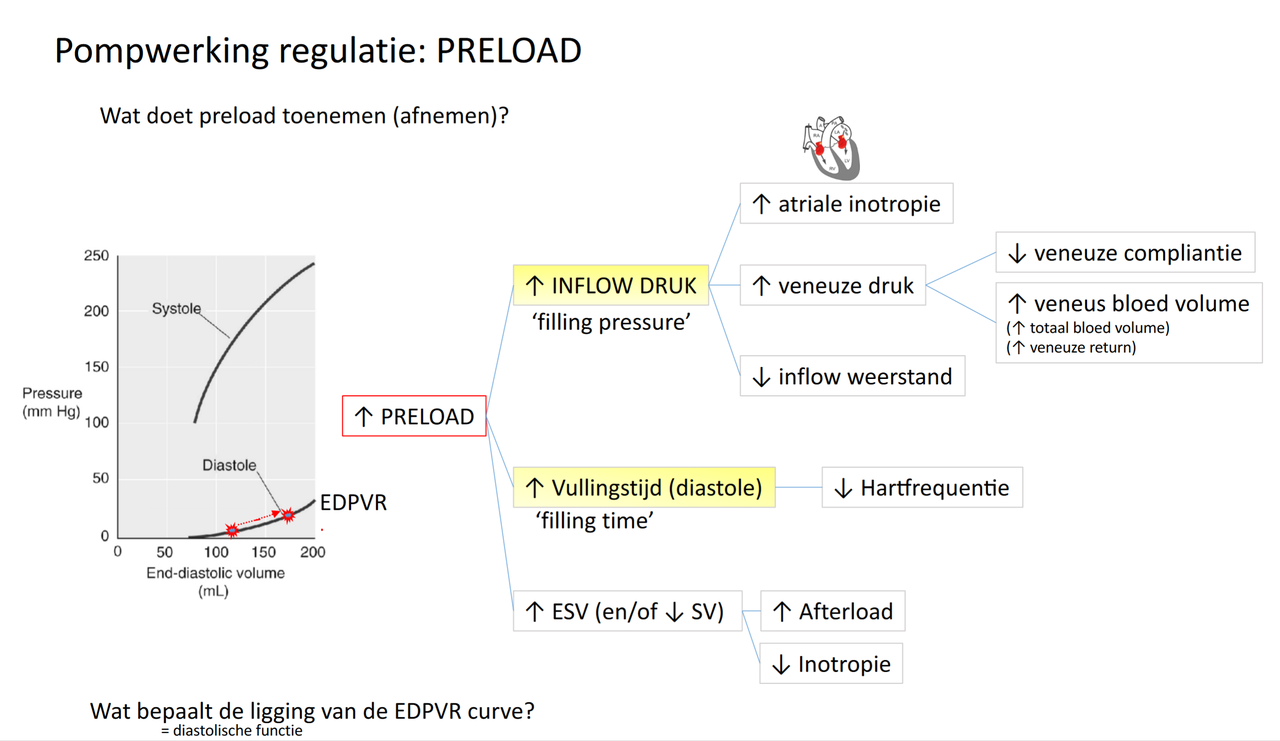
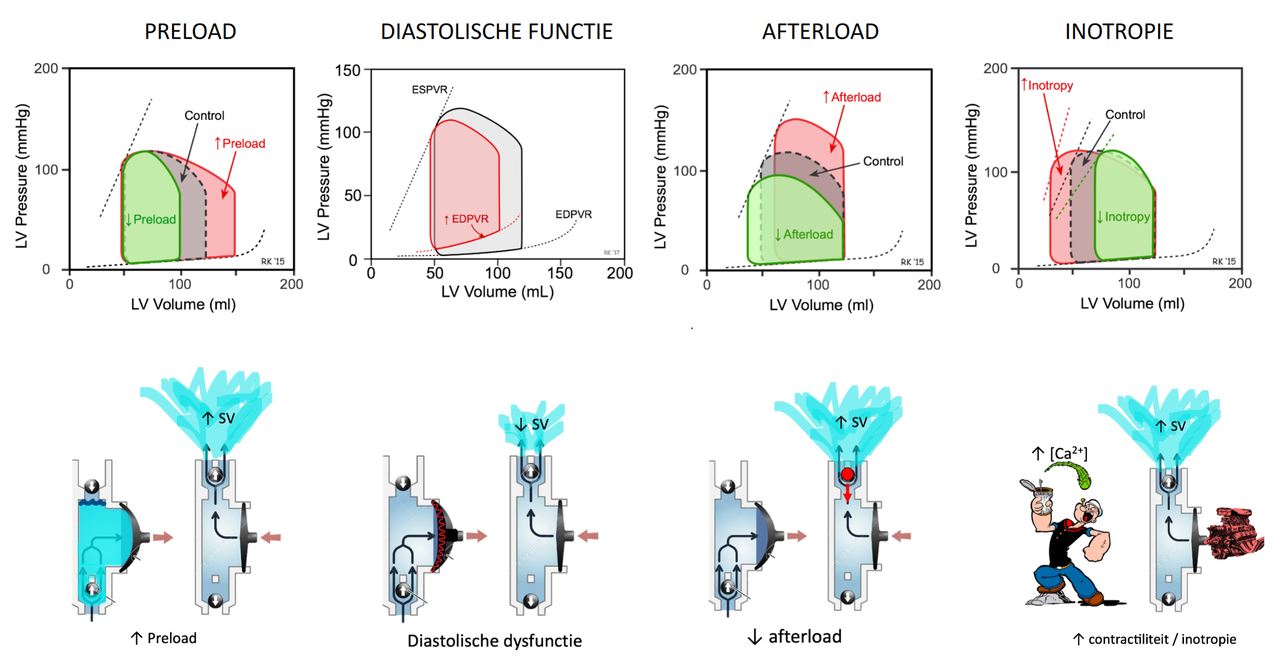
- cf. membraanpomp
- P = f(V)
- 4 hoofdbegrippen
- preload = EDV
- factoren
- vullingsdruk
- tijd
- preload ~ SV (Frank-Starling)
- factoren
- diastolische functie
- EDPVR lijn
- ventriculaire component
- compliantie
- concentrische hypertrofie
- bv. bij aortaklepstenose
- excentrieke hypertrofie
- lusitropie = snelheid relaxatie
- dP/dt
- afh. van Ca2+ pomp
- pericardiale component
- tamponade: veel vloeistof in pericard
- ventriculaire component
- lager SV
- EDPVR lijn
- afterload = MAP | MPAP
- tegendruk semilunar valve
- "te overwinnen arteriele druk"
- hoe meten?
- (gemakkelijk)
- Laplace
- (beste manier)
- lager SV
- systolische functie = contractiliteit = inotropie
- Ca2+
- ESPVR lijn
- hoe meten
- dP/dt
- inotropie ~ SV
- factoren
- positief
- sympatisch
- catecholamines
- afterload
- HR
- negatief
- Ca2+ blockers
- receptor blocker
- ...
- positief
- preload = EDV
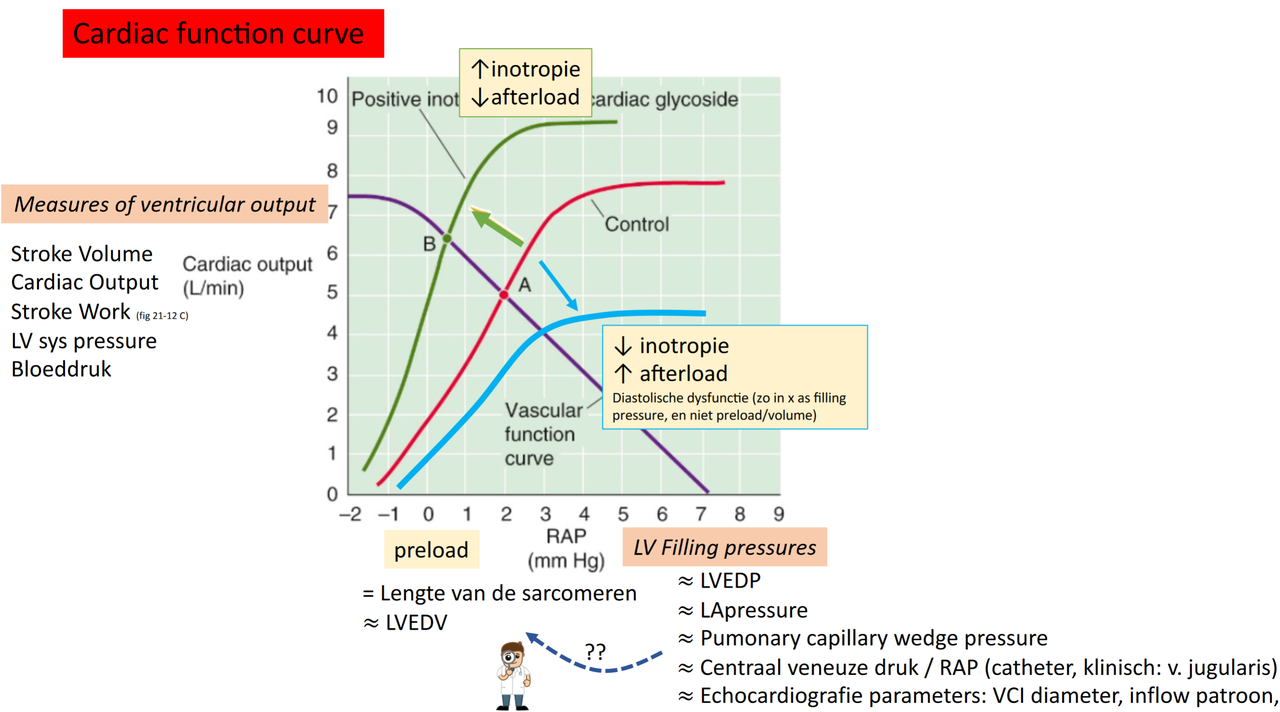
- cardiale functiecurve
- veralgemening Frank-Starling
- x-as
- eerste keuze: preload
- niet praktisch
- LV vuldruk
- P_RA
- LVEDP
- P_LA
- ...
- LV output
- CO
- SV
- stroke work
- LVESP?
- BP
- naar boven als
- inotropie up
- afterload down
- anders naar onder
- eerste keuze: preload
- interactie (ter info)
- preload up -> afterload up
- afterload up -> preload up
- inotropie up
- preload down
- afterload up
23 Regeling bloeddruk en hartdebiet
- 5 vitale params
- HR
- BP
- hypertensie (>140/90)
- hypotensie (<90/60)
- shock = weefsel hypoxie
- distributieve ~ -> SVR down
- e.g., septische shock
- hypovolemische ~
- effectief circulerend volume (~= ECF) down
- ECF ~ CO
- cardiogenische ~ -> SV down
- obstructieve ~ -> SV down
- e.g., tamponade
- distributieve ~ -> SVR down
- shock = weefsel hypoxie
- SO2
- respiration rate (RR)
- temp
Korte termijn - MAP
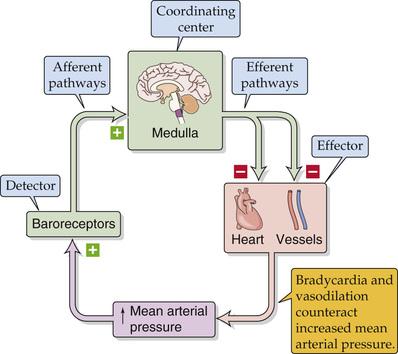
- (chemoreceptor -> secundair)
- geen leerstof
- heel lage pO2 -> ... -> HR up
- baroreceptor -> primair
- locatie detectoren
- sinus caroticus
- n. glossopharyngeus (IX)
- arcus aortae
- n. vagus sinistra (X)
- minder belangrijk
- sinus caroticus
- te hoge druk -> vasodilatie -> SVR down
- geen signaal -> vasoconstrictie
- hypersensitivity -> syncope
- sigmoid curve: firing rate = f(P)
- meest gevoeling rond 95 mmHg
- chronische hypertensie -> schuift op
- coordinator: medulla oblongata
- locatie detectoren
- effectors
- hart
- ortho
- NE -> (enkel in hart!)
- chronotropie () up -> HR up
- dromotropie (geleidingssnelheid) up
- inotropie (contractiliteit) up -> SV up?
- lusitropie (relaxatiesnelheid) up
- para
- n. vagus -> ACh @ M2 (muscarine)
- chronotropie down
- dromotropie down
- minder belangrijk
- ortho
- bloedvaten (herhaling)
- ortho
- NE ->
- vasoconstrictie -> SVR up -> MAP up
- para
- n. vagus (ACh) -> ACh @ M2
- minder belangrijk
- (adrenaline ( receptor): muscles + coronaries)
- ortho
- hart
- carotis massage
Korte termijn - CO
- CO = HR x SV
- geen directe feedback loop voor CO
- indirect
- baroreceptoren
- chemoreceptoren: CO down -> pO2 down -> HR up
- stretch receptoren in atria
- CO ~ ECF (zie onder)
- trigger: te veel volume
- oplossing?
- atrial natriuretisch peptide (ANP) vrijzetting
- vasodilatatie
- diurese
- ECF down
- CO down
- MAP down
- atrial natriuretisch peptide (ANP) vrijzetting
- intrinsiek
- HR: /
- SV
- Frank-Starling: EDV ~ SV
- HR ~ contractiliteit (Bowditch)
- [Afterload ~ contractiliteit (Anrep)]
- extrinsiek
- neuraal (ANS)
- hormonaal
- CO ~ effectief circulerend volume (~= ECF)
- baroreceptor feedback loop
- Frank-Starling: EDV ~ SV
- Bainbridge: atriale vulling ~ HR
Matching venous return met hartdebiet (CO)
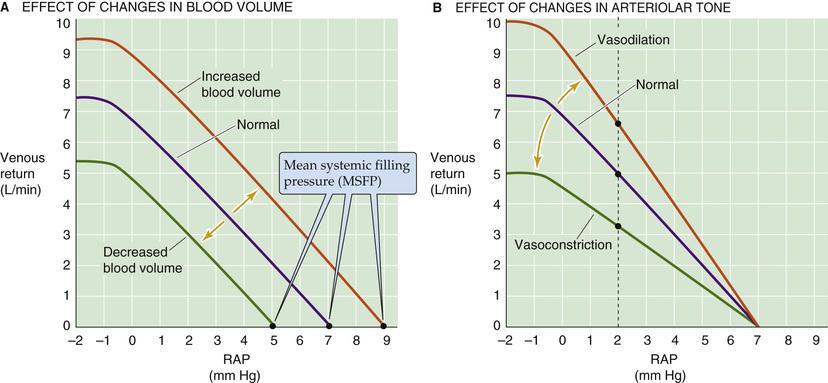
- venous return (VR)
- centraal veneuze druk (CVP)
- druk RA (RAP)
- veneuze weerstand ()
- vasculaire functie curve
- CO up -> RAP down
- RAP = f(VR)
- helling ~ impedantie
- plateau bij RAP < -1 mmHG -> vein collapse
- steady state: CO = VR
- VR up -> RAP down
-
- cf.
- cf.
- CVP ~ bloedvolume of venomotor tonus (Cv)
- e.g., bloedverlies (-) of transfusie (+)
- verschuiving curve
- MSFP gewijzigd
- venous reservoir
- compensatie voor veranderend bloedvolume
- waar?
- huid
- darmen (splanchisch)
- hoe
- vasoconstrictie
- vasodilatie
- CVP ~ arteriolaire tonus
- dilatatie -> CVP up
- constrictie -> CVP down
- kanteling curve
- MSFP ongewijzigd
- match met cardiale functie curve
- snijpunt
- stabiel evenwicht, zelfherstellend
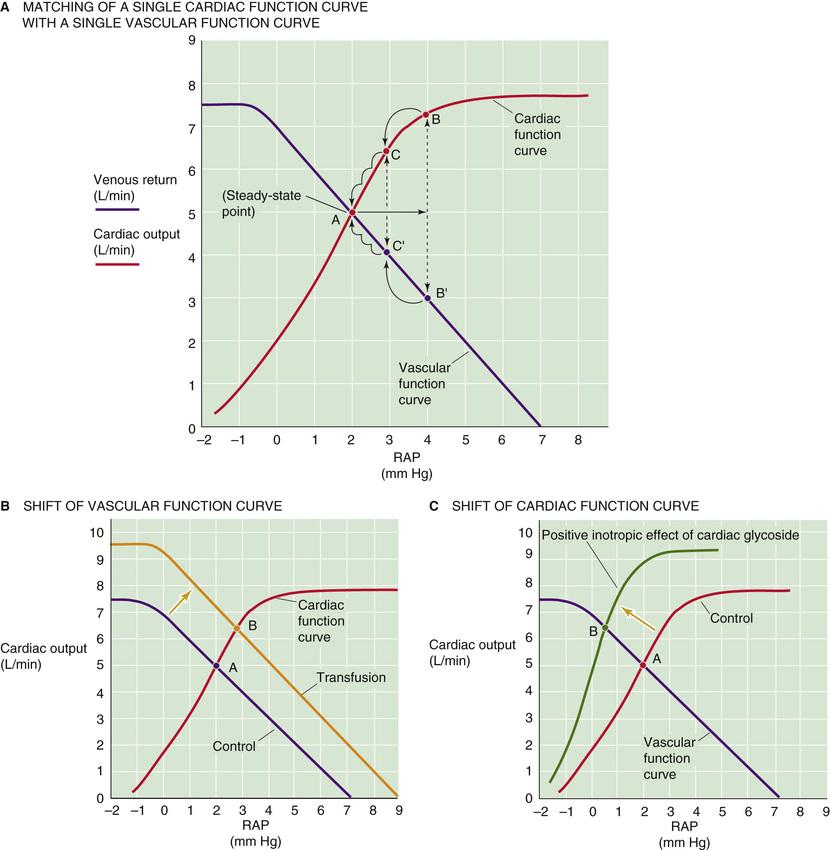
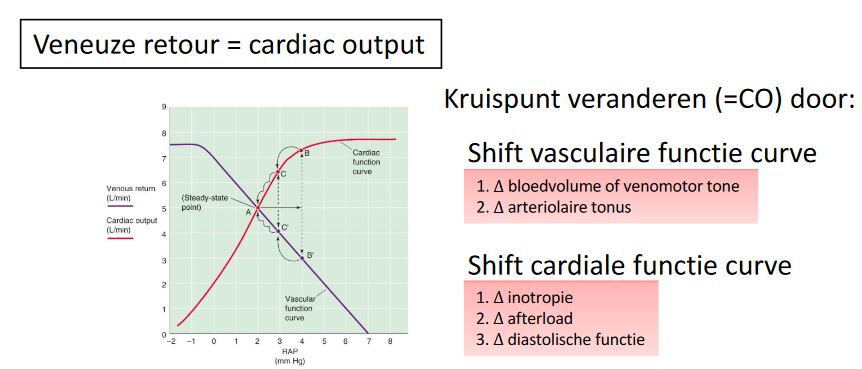
Lange termijn
- vasoactieve stoffen + neuraal
- vasomotor tonus
- ECF via nieren (RAAS)
- ECF = plasma (20%) + interstitieel (80%)
- V ~ P als C constant
- via zout (Na+)
- want CO ~ ECF

- herhaling
- SV ~ PP
- C_aorta ~ PP
- CO = HR x SV
- VR ~ EDV
- effectief circulerend volume ~ ECF
- CO ~ ECF
- Frank-Starling: EDV ~ SV
- Bainbridge: atriale vulling ~ HR
- baroreceptoren
- P up -> SV down
- P down -> HR up
- CO = VR (steady state)
- CO up -> RAP down
24 Bijzondere circulaties
Hersenen
- 2% BW vs 15%
- 100% oxidatief metabolisme
- gevoelig voor hypoxie
- bevloeiing
- toevoer: cirkel van Willis
- 2x a. carotis interna
- 2x a. vertebralis -> a. basilaris
- afvloei: v. jugularis interna
- geen lymfevaten
- toevoer: cirkel van Willis
- BBB
- continu capillair
- tight junctions
- dense basaal membraan
- uitzondering: rond ventrikels
- doorlaatbaar: O2, CO2, water, glucose (gefaciliteerd)
- intercranial pressure (ICP)
- vast V binnen schedel
- cerebral perfusion pressure
- cf. perfusiedruk
- meestal kunnen we CVP negeren
- nu moeten we wel ICP in rekening nemen
- cf. perfusiedruk
- ICP up
- vein collapse
- CPP down
- controle druk
- neuraal: zwak
- lokale controle
- metabool
- neurale activiteit
- ATP afbraak -> adenosine -> vasodilatie
- PO2 down -> vasodilatie
- toepassing: hyperventilatie -> vasoconstrictie -> duizelig
- neurale activiteit
- myogeen
- P_transmuraal -> vasoconstrictie
- metabool
- Cushing reflex
- normaal: ICP up -> hypoperfusie
- o.a. bij hersenoedeem
- beschermt hiertegen via MAP up
- triad
- SBP up
- pulse down
- respiration rate down
- normaal: ICP up -> hypoperfusie
Hart
- 0.5% BW, 5% Q
- heeft veel O2, ATP nodig
- substraten
- free fatty acids (FFA)
- glucose
- lactaat (vooral bij inspanning)
- pyruvaat / ketonen
- bevloeiing
- aanvoer: coronairen
- vooral flow tijdens diastole (80%)
- probleem: HR up -> diastole korter
- compenseert endo vs epicardiale druk bij systole
- vooral flow tijdens diastole (80%)
- afvoer: sinus coronarius -> RA
- collaterale circulatie
- angiogenesis bij trage stenosevorming
- high density
- aanvoer: coronairen
- controle druk
- myogene autoregulatie
- Q ~ QO2 lineair door autoregulatie
- via coronaire reserveflow
- metabool (primair)
- neuraal (secundair)
- ortho
- hart: NE ->
- chronotropie up
- inotropie up
- BV: NE ->
- vasoconstrictie
- hart: NE ->
- para / vagus
- weinig effect
- ortho
- hormonaal
- coronairen: EPI ->
- vasodilatie
- coronairen: EPI ->
- myogene autoregulatie
- balans O2
- verbruik
- rust -> inspanning: x9
- verbruik ~ E_contractie x HR
-
- vooral derde term
-
- factoren
- HR
- inotropie
- afterload
- (preload)
- EDV up -> r ~up -> T up -> E up
- meten: Fick
- QO2 = MVO2 = CBF x (CaO2 - CvO2)
- CBF = coronary blood flow?
- schatten: QO2 ~ HR x SBP
- toevoer
- = flow x #O2
- flow
- r
- P
- R
- HR -> tijd in diastole
- collateralen
- (ml/dl) = SaO2 x 1.35[Hb] + 0.003PaO2
- flow
- = flow x #O2
- ischemie
- hypoxie -> anaeroob -> lactaat -> angina pectoris
- medicatie
- NO -> vasodilatie
- vraag down
- afterload down
- preload down
- toevoer up
- R down
- vraag down
- betablokkers
- vraag down
- HR down
- inotropie down
- toevoer up
- HR down -> meer diastole
- vraag down
- NO -> vasodilatie
- verbruik
Skelet
- rust -> inspanning: x25-50
- bevloeiing
- feed artery
- regelt R
- buiten spier
- ongevoelig voor vasoactieve producten in spier
- primary arteriole
- terminal arteriole
- regelt R
- cf. precapillaire sphincter
- capillaries
- feed artery
- autonome regeling
- balans
- ortho: NE -> -> constrictie
- endo + shear stress -> NO -> dilatatie
- ortho: EPI -> -> dilatatie
- balans
- spierpomp
- vooral effect op venen
- ook op arteries
- P_v down -> dP_cap up -> Q up
- max flow tussen contracties (cf. hart)
- vooral effect op venen
GI
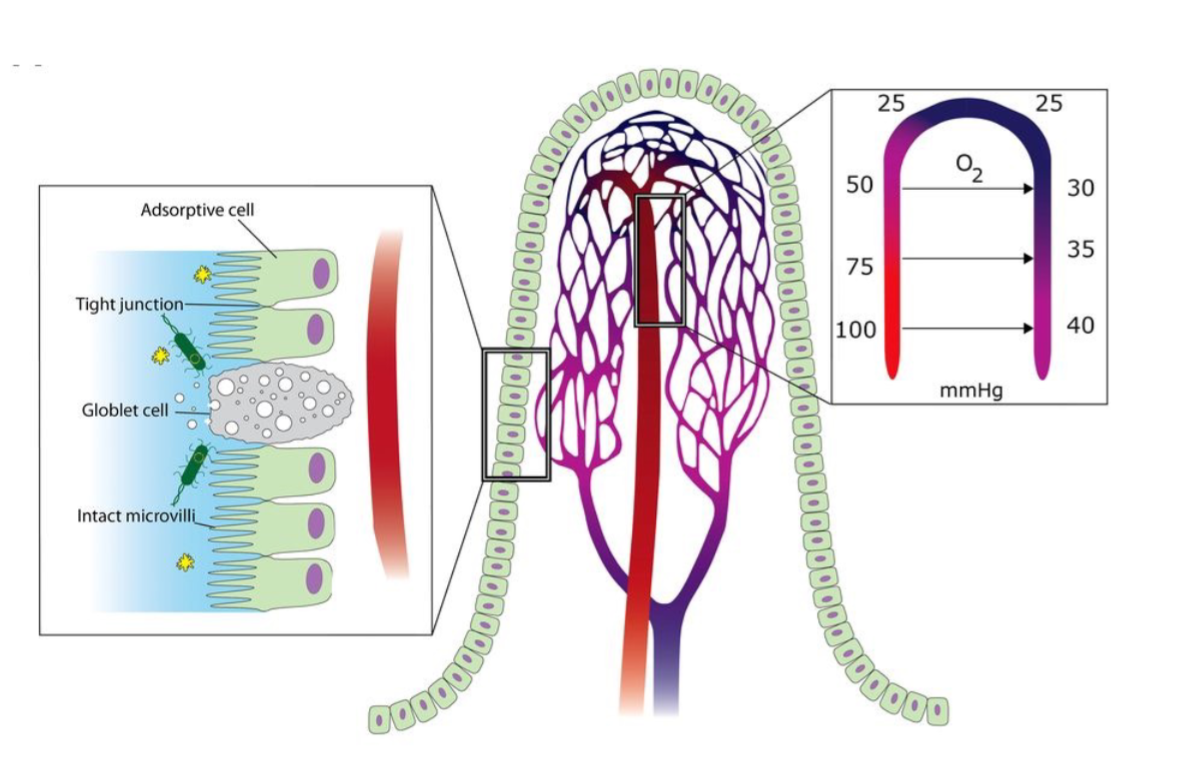
- bevloeiing
- a. coeliaca (truncus?)
- a. mesenterica sup./inf.
- v. portae
- anastomoses
- capillairen
- fenestrae
- groot oppervlak
- counter-current exchange O2
- in villus
- diffusie A -> V
- laagste pO2 in tip
- risico op ischemie
- na maaltijd: Q up -> diffusion down
- regulatie: postprandiale hyperemie
- Q x8 tot 2-4u na maaltijd
- factoren
- ANS
- ortho: NE -> -> constrictie
- para: geen effect op bloedvaten (wel op GI)
- enterisch ZS -> peristaltiek -> pO2 down -> adenosine -> dilatatie
- lokale hormonen
- ANS
- volgorde: maag -> distaal
- bloedreservoir (15%)
- helpt bij regeling SVR
- inspanning/bloeding -> constrictie
- sporten na eten -> krampen
- lever
- bevloeiing
- 75% v. portae
- O2 arm
- zeer lage R
- 25% a. hepatica
- hoge R
- sinusoidale capillairen
- 75% v. portae
- portale hypertensie
- bij cirrose
- varices
- ascites: vocht in abdomen
- bevloeiing
Huid
- functie
- barriere
- thermoregulatie
- T ~ Q
- controle: ANS > lokaal
- apical skin
- neus, lippen, oren, handen, voeten
- hoge A/V ratio
- glomus lichaampjes
- A-V anastomoses
- warmte uitwisseling
- non-apical skin
- geen glomus
- toepassing: photopletysmography (PPG)
- Q sensor vinger
Vergelijking regeling
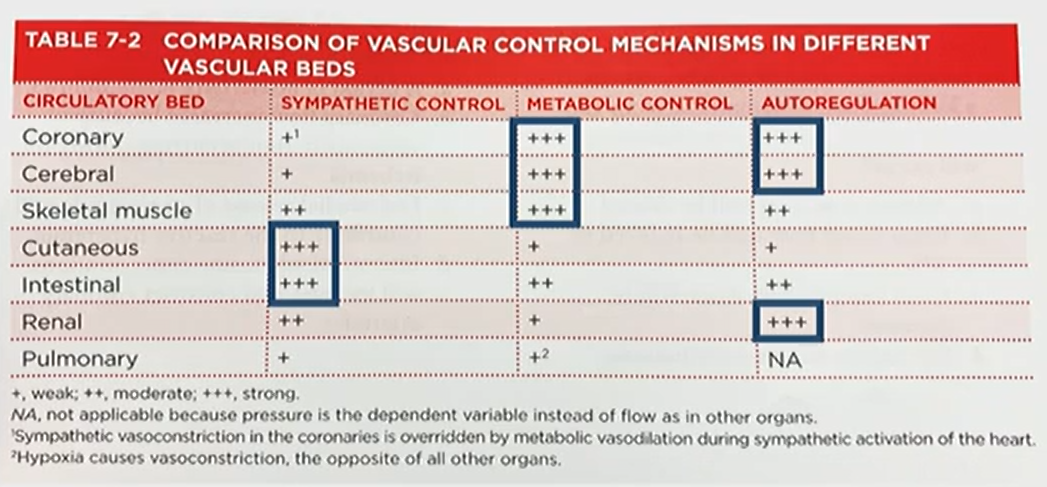
- belangrijkste organen (hersenen, hart, nier): sterke intrinsieke autoregulatie
| Orgaan | Lokaal | Centraal |
|---|---|---|
| hersenen | metabool/myogeen | zwak |
| hart | metabool/myogeen | minder |
| skeletspier | endotheel | ANS: ortho |
| GI | lokale hormonen | ANS, ENS |
| huid | zwak | ANS |
25 Integratieve fysiologie
Interactie
- complexe feedback loops
- doet niet altijd wat je verwacht
4 stresses
Rechtopstaan = orthostasis
- ANS: orthostatische respons
- MSFP: 7 mmHG
- compliantie: 0.02/mmHg
- +2% bloed (100ml / 5l) -> +1 mmHg
- zonder compenstatie: 2.2l pooling in OL
- probleem met VR en dus CO
- orthostatische hypotensie
- orthostatische syncope
- erger bij warm weer
- lagere R huid
- oplossing: orthostatische respons
- RAP: - 22 -> +2 mmHg
- pooling: 2.2l -> 0.5l
- hoe
- 1) niet-uniforme verdeling bloedvolume
- groot volume in thorax
- 2) niet-uniforme compliantie: 0.01 / mmHg in OL
- 3) spierpompen
- verhoogd in OL
- gelijk in abdomen
- dus bloed gaat naar thorax
- 4) autonome reflexen op VR down - HR up - inotropie up - SVR up - P_v up
- 1) niet-uniforme verdeling bloedvolume
Emotionele stress
- fight or flight
- cortex
- hypothamalus
- endocrien
- ADH up
- cortisol up
- medulla oblongata
- skeletspieren: vasodilatatie
- hart
- HR up
- SV up
- => MAP up
- bijnier
- EPI
- ...
- EPI
- ...
- endocrien
- hypothamalus
- cortex
- vasovagale syncope
- trage pols
- cortex
- hypothalamus
- ADH
- medulla oblongata
- (ortho)sympa -
- SVR -
- vagal +
- CO -
- VR -
- => MAP -
- (ortho)sympa -
- hypothalamus
- soms met hyperventilatie
- pCO2 -
- Q -
Inspanning
- CO x5
- HR x3
- SV x1.5
- vroege component: CNS
- zie fight or flight
- late component: spier effecten
- mechanisch: spierpomp
- VR up
- RAP up
- EDP up
- EDV up
- SV up
- CO up
- chemisch
- pO2 down
- vasodilatatie
- MAP down
- baroreceptor
- SV up
- HR up
- vasoconstriction (inactive muscles + other systems)
- CO up
- mechanisch: spierpomp
- herverdeling (hogere) CO
- 15% -> 3% hersenen (zelfde absolute volume)
- 5% -> 5% hart
- 25% -> 3% darmen
- 20% -> 2% nier
- 20% -> 85% spier
- 5% -> 0% huid
- 10% ?
- type inspanning
- dynamic (lopen)
- SBP: 160 mmHg
- DBP: 80 mmHg
- isometric = heavy static (lifting)
- SBP: 250 mmHg
- DBP: 180 mmHg
- dynamic (lopen)
Bloeding
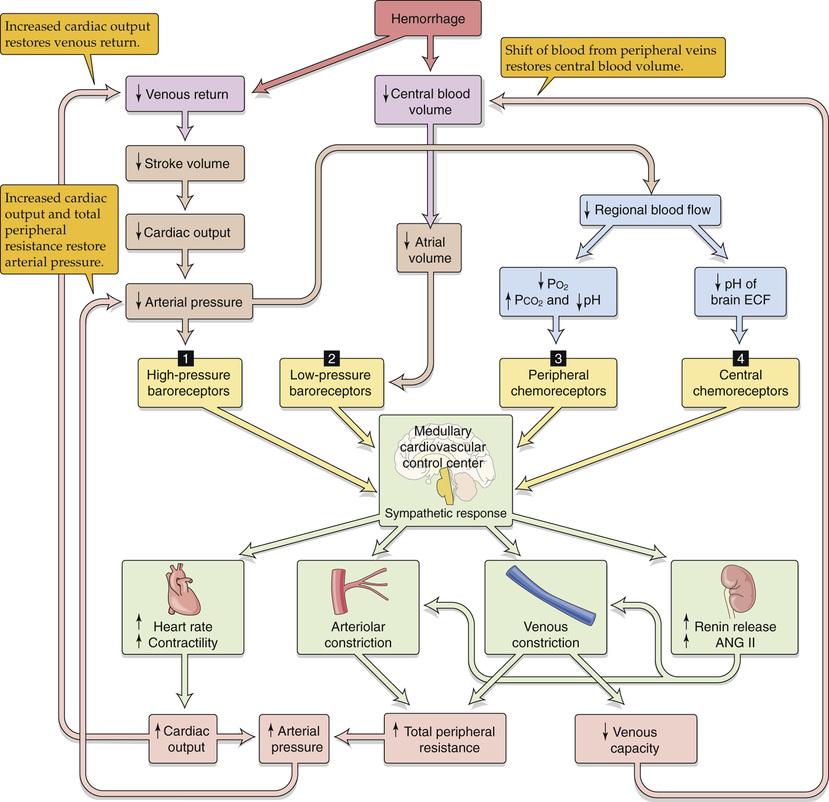
- vascular function curve: schuift on naar links
- nieuw snijpunt
- lager CVP + lager CO
- nieuw snijpunt
- MAP down
- 30% verlies -> hypovolemische shock
- weefsel hypoxie
- SBP < 90
- MAP < 70
- bewusteloos met snelle pols (cf. vasovagale syncope)
- compensatie
- BD herstellen
- tot 20% verlies kan gecompenseerd worden zonder verlaging BP
- wel verlaging CO
- low pressure baroreceptoren @ atrium
- ortho +++
- ADH
- nieren: vasoconstrictie + RAAS
- HR +
- inotropie +
- vasoconstrictie (A+V)
- => SVR up
- MAP up
- ortho +++
- cardiac function curve
- CO hersteld
- lager CVP
- tot 20% verlies kan gecompenseerd worden zonder verlaging BP
- bloedvolume herstellen
- vocht uit interstitium
- Starling
- oppassen: dilatie -> laag hematocriet
- zelf-limiterend wegens osmose
- lever/GI: meer proteinen
- albumine synthese
- Starling
- minder verlies via nier
- dorst: meer vochtinname
- vocht uit interstitium
- BD herstellen
Herhalingsles
- extra leerstof!