Skip to main content
- symbols
-
radius
-
hight
-
length
-
area
-
volume
-
force
-
pressure
-
flow
-
density
-
flow speed
-
viscosity
-
shear rate (schuifsnelheid)
-
shear stress (schuifspanning) [Pa]
-
resistance
-
inertance
-
compliance
-
impedance
-
frequency
-
wave speed
-
strain (rek/Elongatie)
-
stress (wandSpanning) [Pa]
-
Young's modulus:
-
wall tension ("spanningskracht") [Pa m]
17 Hemodynamics
Organization of the Cardiovascular System
Hemodynamics
- sphygmomanometer: measure blood pressure
- area [m2]
- density
- blood: 1050 kg/m3 = 1.05 g/ml
- pressure [N/m2 = Pa or mmHg or cmH2O]
- hydrostatic pressure
- use to compute in mmHg$
- 1 mmHg = 133 Pa
- flow speed [m/s]
- flow [l/min or m3/s]
- e.g., cardiac output Q = CO = 6 l/min = 100 cm3/s
- e.g.,
- viscosity [Poise: 1 P = 0.1 Pa.s]
-
-
-
(formularium)
- kinematic viscosity:
- resistance [Pa.s / m3]
- series:
- parallel:
- conditions: ...
-
-
- cardiac output flow
- heart rate
- stroke volume
- cf.
- MAP = systolic BP + diastolic BP
- blood flow in smaller vessels
- Fahraeus-Lindqvist effect
- RBCs near center
- plasma near walls
- branch: plasma skimming -> lower hematocrit = bad
- solution: arterial cushions near branches
- capillaries: RBCs deform
- Bernoulli equation
- cf. inertia
- cf. conservation of energy
- assumptions
-
const
-
- implication
- measure pressure with invasive catheter
- upstream: decceleration, higher pressure, incorrect
- downstream: acceleration, lower pressure, incorrect
- opening to side: correct measurement
- application: estimate valve stenosis surface area
- application: arterial stenosis
- semi-empirical law
-
- 80% -> 90% stenosis: 5x higher pressure drop
- continuity
-
constant in closed system
-
- measurements
- pressure
- non-invasive
- indirect
- sphygmomanometer
- applanation tonometry
- venous pressure of v. jugularis
- VCI diameter
- ultrasound
- P = f(VCI diameter, collapse, breathing)
- direct
- invasive
- indirect
- catheder via v. jugularis -> right heart
- "pull back"
- wedge pressure -> LA
- direct
- catheder
- via a. radiualis
- via v. jugularis -> right heart
- upstream vs downstream difference
- RA, RV, pulmonary artery
- via a. iliaca -> left heart
- flow
- strategies
- non-invasive
- indirect
- direct
- ultrasound (also speed with Doppler)
- nuclear imaging (only volume)
- MRI (also speed)
- CT (only volume)
- ?
- cardiac ultrasound
- 1D, 2D: assume ventricular geometry
- 3D: no assumptions
- invasive
- indirect
- direct
- perivascular methods
- electromagnetism
- movement of conductor (blood) induces voltage in magnetic field
- ultrasound
- ?
- Fick's method
- add known quantity to fluid
- measure concentration before and after
- golden standard
- thermodulution: ~Fick, but with temperature instead of concentration
- LV angiogram
- resistance
How Blood Flows
Laminar
-
- concentric layers
- parabolic front
- silent
- Poiseuille law
- conditions
- incompressible
- rigid cylindrical tube with radius
- no slippage at wall
- laminar, steady flow
- constant
- Newtonian fluid
- water, plasma: OK
- blood: not at lower velocity due to RBC
- flow speed
-
: viscosity
-
: length
-
: radius
- parabolic profile
-
(center)
-
(near wall)
-
- resistance
Turbulent
-
- blunted front
- noisy -> murmurs
- when
- large vessels
- high
- e.g., arterial stenosis or exertion
- low
Origins of Pressure in the Circulation
- hydrostatic pressure
- in direction of gravity
-
- heart: height
- recumbent vs upright
- recumbent: no hydrostatic pressure
- upright: hydrostatic pressure
- more on feet
- less on head (relative to heart)
-
is same in both scenarios
- driving pressure not impacted
- so remains constant
- axial/driving pressure
- causes blood flow
- viscous resistance
- inertia
- Bernoulli: higher , lower
- pulsating flow
- fluid briefly keeps moving forward even under negative pressure
- inertance
-
- more important than in large vessels
- compliance
- transmural pressure
- perpendicular to axis/wall
- governs vessel diameter
-
-
rigid, no change in volume possible
18 Blood
Blood viscosity
- shear rate (schuifsnelheid)
- shear stress (schuifspanning) [Pa]
- viscosity [P = Pa s]
- Newtonian fluid: constant
- e.g., water, plasma, ~blood in large vessels
- Einstein:
-
: hematocrit
- not very accurate
- non-Newtonian fluid: variable
19 Arteries and Veins
The arterial distribution and venous-collection systems
- distribution
- 84%: systemic
- 14% in arteries
- 6% in capillaries
- 64% in veins
- 9%: pulmonary
- 7%: heart
- pressures (mmHg)
- systemic
- aorta: 95
- arterioles: 60
- capillaries: 25
- venules: 15
- veins: 3-15
- pulmonary
- artery: 15
- capillaries: 10
- veins: 5
- largest drop in arterioles
- control of capillary pressure
Elastic properties of Blood Vessels
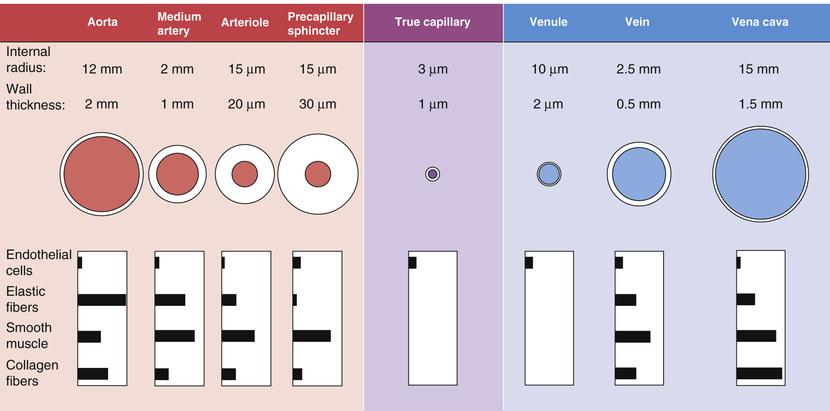
- vessel wall
- 4 layers
- endothelium
- only layer in small vessels
- no active components
- intima
- media
- smooth muscle
- active component
- mostly in arterioles + sphincters
- adventitia
- passive components
- elastine
- collagen I/III: less elastic
- arteries vs veins
- arteries
- relatively more elastine -> less rigid
- resistance vessels
- ~constant compliance
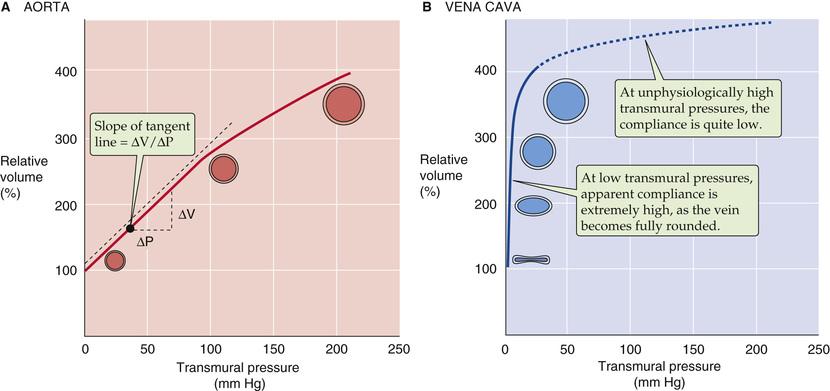
- veins
- high compliance at very low pressures
- not because of elastine
- because of geometry: flat -> filled tube
- low compliance at very high pressures
- capacity vessels
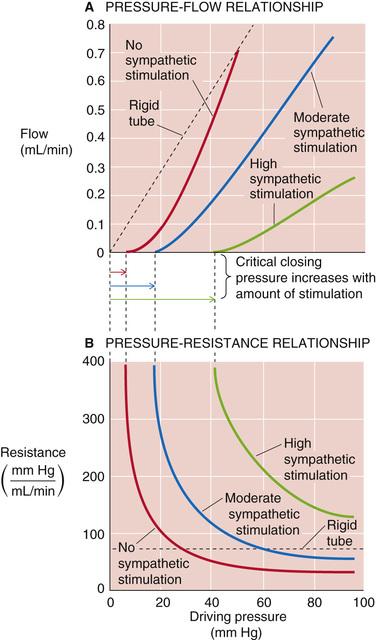
- rigid vs elastic vessel
- rigid: Poiseuille (see above)
-
(linear relation)
-
constant
- elastic
- non-linear relation between and
- also depends on activity of smooth muscles
- "sympathetic stimulation"
- increases "critical closing pressure"
- more needed to have any flow at all
- vasoconstriction and vasodilation
- regulate blood distribution
- strain (rek)
- strain rate
- stress (wandspanning) [Pa]
- stress-strain:
- cf. Hooke's law:
-
: Young's modulus = elastic modulus [Pa]
- wall tension ("spanningskracht")
- force per unit length
-
[Pa m]
-
: tissue pressure (at outside tube wall)
-
: intravascular pressure
-
: tube radius (without wall?)
- does not include wall thickness
- highly correlated with elastine presence
- different between aorta and vena cava due to elastine
- Laplace stress (wandspanning) [Pa]
- alternative for wall tension
- force per area
- tube
- length
- radius
- wall thickness
-
-
-
- sphere:
- age
- stiff vessels (more collagen)
- impact of smooth muscles
- adapts wall tension
- peaks at 190% relative radius
- -> stable vessels (no blowout, no collaps)
- pulsating flow
-
curve curve
- effect of impedance (= resistance + compliance + inertance)
- frequency dependent
-
- lower frequencies -> compliance, negative phase angle
- higher frequencies -> mostly
- windkessel effect
- heart has intermittent output
- vessels have pulsative yet continues forward flow
- how? aorta's compliance acts as buffer
- clinical relevance
- stents have little compliance
- careful with usage in large vessels close to heart
- waves
- background info for chapter 22
- pressure wave
- flow wave
- wave speed
-
> flow speed
- frequency dependent
- lower C ~ higher c
- e.g. in older people
- e.g. in peripheral vessels
- reflections
- e.g. at aorta bifurcation
- superposition: changes upstream pressure wave
- augmentation index (AI)


