Celbiologie I (2022-2023)
- Praktisch
- Formularium
- Basics of organic chemistry
- H1 Preview
- H2 Chemistry of the cell
- H3 Macromolecules
- H5 Bioenergetics
- H5bis Bioenergetics
- H6 Enzymes
- H9 Glycolysis and fermentation
- H10 Aerobic respiration
- H11 Photosynthesis
- H16 DNA and chromosomes
- H17 DNA replication and error correction
- H18 transcriptie
- H19 translatie
- H20 regulatie
- H21 methods
- H24 mitose
- H25 meiose
- H26 kanker
- Practicum 1 - fotometrische dosage van eiwitten
- Practicum 2 - DNA: structuur, amplificatie en restrictiedigestie, gelelektroforese
- Practicum 3 - koolhydraten en lipiden
- Practicum 4 - enzymkinetica
- Practicum 5 - structuur macromoleculen
- Werkzitting 1
- Werkzitting 2
- Werkzitting 3
- Werkzitting 4
- Werkzitting 5
- Werkzitting 6
Praktisch
- 11stp (oud curriculum)
- eerste semester
- docenten
- prof. A. Van Eynde
- prof. M. Bollen
- prof. R. Derua
- handboek: Becker’s World of the Cell (9th)
- onderdelen
- 40 lessen (60u)
- 6 werkzittingen (9u)
- 5 practica (20u)
- verplicht
- labojas meebrengen
- 10% punten
- 3 sessies monitoraat (4.5u)
- examen
- 90% punten
- 3u
- multiple choice
- 60 vragen?
- geen rekentoestel
- dus ook geen formules uitwerken
- wel formules herkennen
- https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1OrHen5XHsQ2YURugr6Fx5F_mZAH2OKId
Formularium
- tabel met codon-AZ mapping wordt gegeven indien nodig
- Lineweaver-Burk plot
- Eadie-Hofstee plot
- Hanes-Woolf
- gasdichtheid bij STP: 22.4 L/mol
- G(ATP): -7.3
Basics of organic chemistry
- TODO methyl, acetyl, acetone, formaldehyde, ...
- functional groups (at neutral pH)
-
- amino:
-
- carboxyl:
- phosphate:
- neutral but polar (due to presence of and )
- hydroxyl:
- sulfhydryl:
- carbonyl:
- in aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, amides, ...
- aldehyde:
- unclassified
- acyl:
- oxoacid that lost 1 or more groups
- acyl:
-
- classes
- ester:
- ether:
- thio-ether:
- aldehyde:
- ketone:
- amine
- thiol:
- thial:
- phosphate:
- oxoacid: acid that contains
- carboxylic acid: =
- deprotonation:
- carboxylic acid: =
- acid-base
- acid:
- : acid
- : conjugated base
-
- Henderson–Hasselbalch equation
- base:
- redox
- oxidation
- donate electrons
- release energy
- e.g.,
- reduction
- accept electrons
- requires energy
- e.g., photosynthesis
- oxidation
H1 Preview
- cell theory
- all organisms consist of 1 or more cells
- cell is basic unit of structure for all organisms
- all cells arise only from preexisting cells
Strand 1: cytology
- sizes
- small molecules: <1nm
- DNA: 2nm
- microfilament: 7nm
- membrane: 8nm
- microtubule: 25nm
- ribosome: 25nm
- virus: 100nm
- mitochondria: 1um
- bacteria
- nucleus: 10um
- eukaryotic cell: 10-100um
- microscopy
- microtome: cut in small slices
- dyes and stains
- resolution (length): how far apart to see as 2 entities?
- nm
- eye: 0.25mm
- light microscope: 0.25um (1000x)
- electron microscope: 2nm (100 000x)
- types of light microscopy
- brightfield
- requires fixation and (usually) staining -> dead cells
- phase contrast
- alive
- based on subtle phase change of light during refraction
- differential interference contrast
- idem
- fluorescence
- antibody labeling = immunofluorescence
- binds to specific antigen
- primary=direct: C region of antibody is labeled
- secondary=indirect
- primary antibody attaches to antigen
- labeled secondary antibody attaches to primary antibody
- can bind multiple times -> amplify signal -> more sensitive
- green fluorescent protein (GFP) from jellyfish
- antibody labeling = immunofluorescence
- confocal
- focus on 1 plane using LASER
- brightfield
- electron microscopy
- shorter wavelength -> better resolution
- 2 types
- transmission (TEM): through tissue (2D)
- scanning (SEM): 3D effect, only surface
Strand 2: biochemistry
- methods
- isotopes (e.g., C14)
- centrifugation = subcellular fractionation
- chromatography (general term)
- separate mixture of molecules based on charge, size or affinity
- added to system (tube, paper, ...) with stationary phase material
- techniques
- thin layer chromatography (TLC)
- stationary phase: cellulose or silica gel layer
- components travel through layer at different rates
- application/namesake: separating plant pigments
- column chromatography
- stationary phase in tube
- then add mixture
- components will diffuse/sink at different rates
- thin layer chromatography (TLC)
- electrophoresis
- electric field
- separate macromolecules based on mobility (~size, charge) through gel
- useful for DNA, RNA, proteins
- mass spectrometry
- determine size (mass?) and composition of proteins
Strand 3: genetics
- chromosome theory of heredity
- Watson & Crick: DNA double helix
- central dogma of molecular biology: DNA -> RNA -> proteins
- replication
- transcription
- translation
- methods
- recombinant DNA tech
- = DNA from different sources combined
- using restriction enzymes: cleave DNA
- hybridization: make double strand out of two single strands
- sequencing
- bio-informatics
- recombinant DNA tech
- model organisms
- bacterium: Escherichia coli
- 4000 genes
- unicellular, prokaryote
- macromolecule synthesis
- yeast: Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- 6000 genes
- unicellular, eukaryote
- cell cycle
- fruit fly: Drosophila melanogaster
- 13 000 genes
- developmental biology
- roundworm: Caenorhabditis elegans
- 19 000 genes
- developmental biology, aging
- mouse: Mus musculus
- 25 000 genes
- mammal
- human pathologies
- green alga: Chlamydomonas reinhardtie
- unicellular, eukaryote, plant
- Arabidopsis thaliana
- 25 000 genes
- multicellular, flowering plant
- "zandraket"
- bacterium: Escherichia coli
H2 Chemistry of the cell
- calorie (cal):
- energy needed to raise the temp of 1g water with 1K
- bond strength (strong->weak)
- covalent
- visible light photon energy
- hydrogen bond (1/10 strength)
- thermal vibration energy
- covalent
- asymmetric atom: four different groups
- asymmetric atoms give rise to stereoisomers
- examples
- one per amino acid
- D-alanine
- amino group right in Fischer
- L-alanine
- amino group left in Fischer
- both occur in biology, only L-alanine used in proteins
- D-alanine
- four in (linear) aldohexose (see H3)
- one per amino acid
- cell composition
- 70% water
- 30% chemicals
- 15% proteins
- 6% RNA
- 4% ions and small molecules
- 2% phospholipids
- 2% polysaccharides
- 1% DNA
- properties of water
- polar
- cohesive due to hydrogen bonds
- high specific heat and high heat of vaporization due to hydrogen bonds
- excellent solvent
- hydrophilic, hydrophobic or both (amphipathic)
- buffers
- intracellular: en ,
- extracellular: en ,
- membranes
- phospholipids and glycolipids form lipid bilayer
- polar head: hydrophilic
- nonpolar tail: hydrophobic
- permeability (good -> poor)
- nonpolar
- small, uncharged, polar
- large, uncharged, polar
- charged (ions)
- phospholipids and glycolipids form lipid bilayer
- macromolecules
- proteins, nucleic acids, polysaccharides, lipids
- monomer -> polymer
- amino acids -> proteins
- nucleotides -> nucleic acids
- monosaccharides -> polysaccharides
- (lipids are not polymers)
- synthesis: condensation = dehydration (requires energy)
- analysis: hydrolysis (releases energy)
- 3D structure
- self-assembly
- might require chaperones
- hydrophobic hydration
- H bonds
- donor vs acceptor?
- ionic interactions
- hydrophobic interactions
- H bonds
- Van Der Waals interactions
- depends on T, pH
- self-assembly
H3 Macromolecules
Proteins
- nine classes
- enzymes
- structural
- motility
- regulatory
- transport
- signaling
- receptor
- defensive
- storage
- monomer: amino acid (AA)
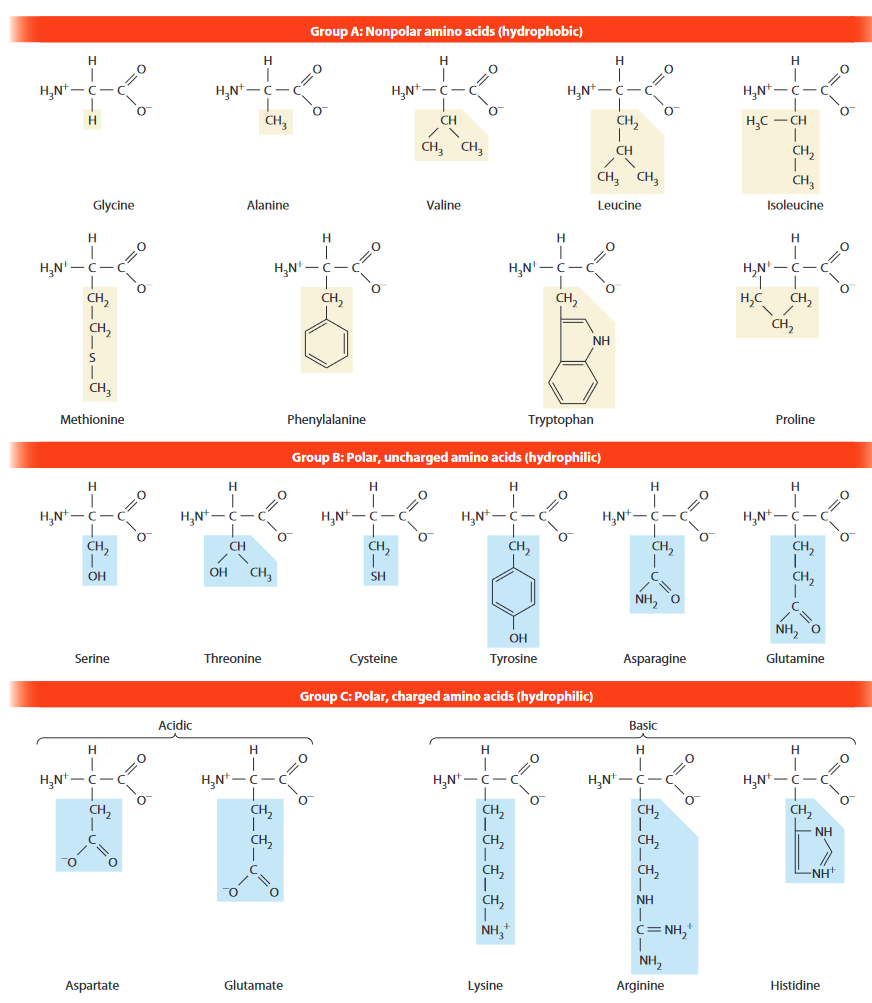
- 20 types used in proteins
- 60+ exist (incl. posttranslational modifications)
- three letter code is usually first three letters of name
- exceptions: Asn (vs Asp), Gln (vs Glu), Ile, Trp
- chiral
- four covalent bonds
- amino group:
- background info
- primary amine , or protonated
- secondary amine , or protonated
- ionized (protonated) at physiological pH
- background info
- carboxyl group:
- ionized (deprotonated) at physiological pH
- atom
-
group
- classification
- 9 nonpolar, hydrophobic, found on inside or in membrane
- Gly, Ala,Val, Leu, Ile, Met, Phe, Trp, Pro
- mostly and
- Met contains
- Trp contains
- Phe and Trp contain aromatic group
- Pro contains secondary () instead of primary amine
- due to ring
- secondary amino acid (formerly imino acid)
- 11 polar, hydrophilic, found on outside
- 6 uncharged
- due to presence of or (or ?)
- Ser, Thr, Cys, Tyr, Asn, Gln
- Cys contains
- Asn, Gln contain
- Tyr contains aromatic group
- 5 charged
- 2 acidic, negative
- Asp, Glu
- due to
- 3 basic, positive
- Lys:
- Arg:
- His:
- can be acidic of basic
- pK=6 when free in water
- at pH=7.4
- 4% : acidic, pH=5.8
- 96% : basic, pH=7.8
- both exists!
- application
- acid-base catalysis in RNase
- pK can shift due to surroundings
- hydrophobic env -> less acidic
- basic env -> more acidic
- stabilize negative charges???
- still good buffer
- can be acidic of basic
- 2 acidic, negative
- 6 uncharged
- 9 nonpolar, hydrophobic, found on inside or in membrane
- classification
- amino group:
- two stereoisomers: L (in proteins) and D
- except Glycine (because )
- four covalent bonds
- polymer: polypeptides and proteins
- peptide bond (covalent)
- amino acids -> polypeptide
- six atoms between are planar due to partial double bond
- i.e., fixed connecting two AA
- exception: can also rotate in Pro
-
terminus and terminus
- created from N -> C during translation
- amino acids become amino acid residues
- cis vs trans
- by default trans: on different sides
- exception: Pro can be cis
- protein: one or more polypeptides with unique, stable 3D structure, active
- monomeric: single polypeptide
- multimeric: multiple polypeptides
- dimer: e.g., insulin
- trimer
- tetramer: e.g., hemoglobin ()
- peptide bond (covalent)
- folding
- into proper shape = conformation
- denaturation and renaturation
- depends on temperature, pH, salt, ...
- caused by bonds and interactions
- between groups of amino acids
- covalent (70-100kcal/mol, 150-200kcal/mol for double/triple bonds)
- anisotropic (why?)
- disulfide bond
- between two Cys that each contain sulfhydryl groups
- oxidation
- intra- vs intermolecular
- non-covalent
- hydrogen bonds (5kcal/mol)
- weak but abundant
- important for alpha helices and beta sheets
- donor: with in e.g., and amino groups
- also those not in R?
- acceptor: atom in e.g., and
- ionic bonds (3kcal/mol)
- long distance, isotropic force
- depends on pH to maintain ionization
- Van Der Waals interactions (0.1-0.2kcal/mol)
- transient dipoles
- close range: < 0.2nm
- important in context of complementary surfaces
- hydrophobic interactions
- hydrophobic inside
- hydrophilic outside
- combination allows compact 3D shape
- hydrogen bonds (5kcal/mol)
- levels
- primary structure
- amino acid sequence
- covalent peptide bonds
- N -> C
- secondary
- Ramachandran diagram
- rotation angles between and resp. N and C
- H bonds in backbone (not sidechains) between and
- alpha helix
- right handed
- intramolecular
- 3.6 AA/turn
- point outward (steric hindrance)
- typical AAs
- Leu, Met: non-polar
- Glu: acidic
- helix breaker
- Pro: side chain interferes with backbone
- Gly: too flexible around
- hydrphobic helices in membranes
- amphipathic helices
- repeats of 2 hydrophobic and 2 hydrophilic AA
- beta sheet
- intra or intermolecular
- parallel or antiparallel
- Ile, Val, Phe: non-polar
- type
- hydrophilic
- hydrophobic
- amphipathic
- on separate sides of sheet
- motifs
- beta-alpha-beta
- hairpin loop (beta-turn-beta)
- helix-turn-helix
- Ramachandran diagram
- tertiary
- based on R-group interactions
- stabilized by disulfide bonds
- also non-covalent bonds
- two types
- fibrous
- secondary > tertiary
- fibroin in silk
- small R groups: Gly, Ala, Ser
- lots of beta sheets
- already max stretched
- creases/wrinkles possible
- keratin in hair
- lots of alpha helices
- extensible
- coiled coil
- hydrophobic R -> tight packing
- lots of alpha helices
- collagen
- Gly, Pro -> left handed helix
- 3x -> right handed helix
- elastin
- globular
- most proteins
- ribonuclease
- domains
- locally folded structure
- separate function
- fibrous
- quaternary
- multiple polypeptides -> multimeric protein
- "subunits" of "chains"
- bonds: = tertiary
- multiple polypeptides -> multimeric protein
- multiprotein complex ("pipeline")
- pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
- primary structure
- insulin
- subunit A (21AZ)
- 1 intramolecural disulfide bond
- subunit B (30AZ)
- 2 intermolecular disulfide bonds
- subunit A (21AZ)
- hemoglobin
- two alpha subunits
- two beta subunits
- sickle cell
- beta subunit: glutamate -> valine (E6V)
- deoxyHb sticks together
- zie werkzitting 1, oef 16
- Alzheimer
- amyloid plaques
- outside neurons, near synapses
- tau polymer
- inside neurons
- neurofibrillary knots
- amyloid plaques
- X-ray cristallography
- prerequisite: primary structure known
- create pure protein crystal
- decrease solubility
- add precipitans (salt?) -> less water
- supersaturated -> crystal
- decrease solubility
- irradiation of crystal at various angles
- result: diffraction pattern
- model construction
Nucleic acids
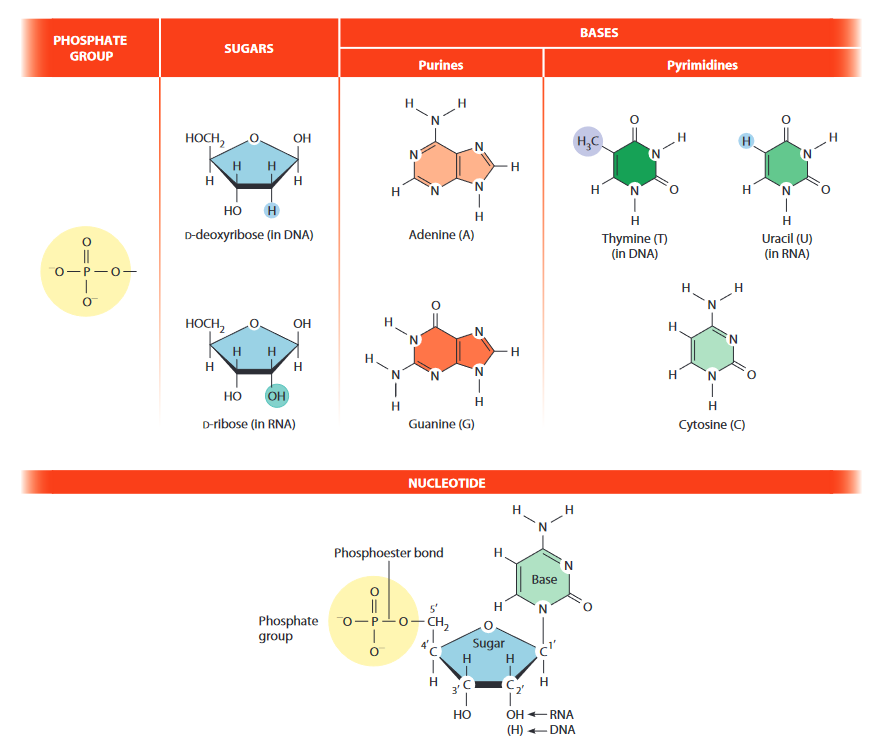
- heterocyclic aromatic bases
- pyrimidines (1 6-ring)
- cytosine (C)
- thymine (T) (DNA only)
- uracil (U) (RNA only)
- purine (6 ring [pyrimidine] + 5 ring [imidazol])
- adenine (A)
- guanine (G)
- somewhat hydrophobic
- alternating double bonds -> resonance -> very stable
- pyrimidines (1 6-ring)
- sugar: aldopentose
- 1' - 5'
- D-ribose
- D-deoxyribose ( instead of at 2')
- nucleoside = base + sugar at 1'
- (deoxy)adenosine
- (deoxy)guanosine
- (deoxy)cytidine
- deoxythymidine
- uridine
- nucleotide = nucleotide + at 5'
- AMP / dAMP
- GMP / dGMP
- CMP / dCMP
-
- / dTMP
- UMP / -
- nucleotide -> polynucleotide = nucleic acid
- phosphodiester bridge
- 5' -> 3'
- terminal 5' has P
- terminal 3' has -OH end
- sugar-phosphate backbone
- charged P
- polar s in ribose
- hydrophilic
- synthesis requires energy and info
- DNA: dATP, dCTP, dGTP, dTTP
- RNA: ATP, CTP, GTP, UTP
- phosphorylated adenosine
- AMP
- 1 phosphoester bond
- A-P
- ADP
- 1 phosphoester bond
- 1 phosphoanhydride bond
- A-P~P
- ATP
- 1 phosphoester bond
- 2 phosphoanhydride bonds
- A-P~P~P
- AMP
- DNA
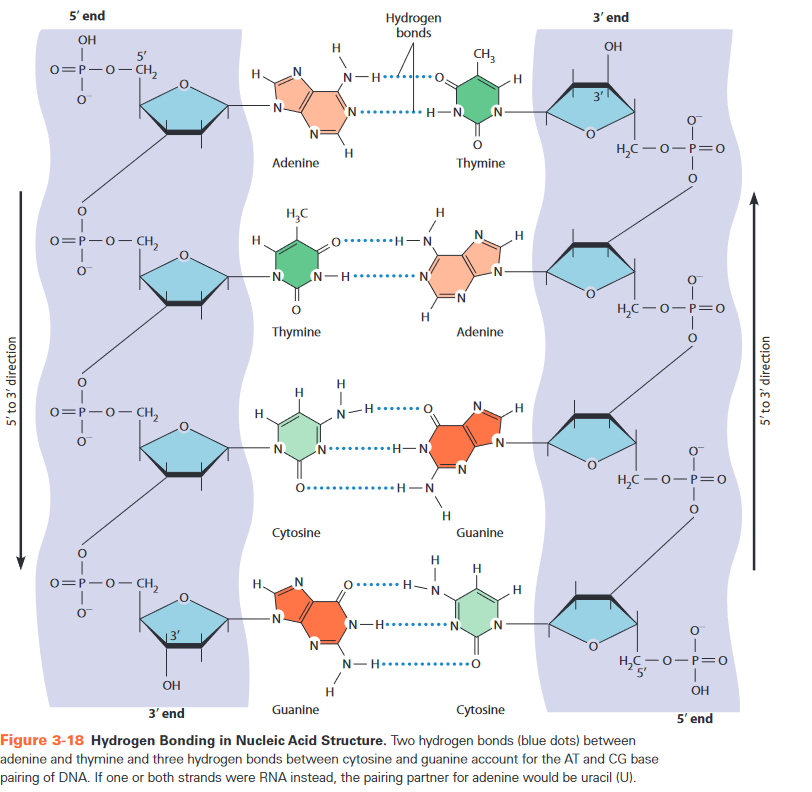
- right-handed double stranded (ds) helix (for B-DNA)
- antiparallel
- 5'->3': coding strand
- 3'->5': template strand = matrijs, from which RNA is transcribed
- roles can be flipped by "rotating DNA"
- complementary base pairing
- purine + pyrimidine (to keep width equal)
- purine + pyrimidine (to keep width equal)
- base stacking
- hydrophobic interactions
- stabalizes structure
- G-C more than A-T?
- major and minor groove
- RNA
- mostly (not always) single stranded (ss)
- ribose less stable in basic environment than deoxyribose
- due to group
- more flexbile -> more functions than DNA
- secondary structure: bind with self
- hairpin
- stem-loop:
Polysaccharides
- background: hemi-acetal and hemi-ketal
- aldehyde:
- keton:
- e.g. aceton = dimethylketon
- alcohol:
- aldehyde + alcohol -> hemi-acetal
- C with 4 groups
- can reduce atoms by oxidation of aldehyde
- (copper reduced from +II to +I)
- C with 4 groups
- ketone + alcohol -> hemi-ketal
- C with 4 groups
- cannot reduce
- but ketose can transform into aldose in weak basic environment
- via enadiol
- C with 4 groups
Monosaccharides
- colloquial: "carbohydrates"
- aldose: terminal carbonyl group
- ketose: internal carbonyl group
- typically at C2 -> 2-ketose
-
- weak basic env helps
- 3-7 carbon atoms
- numbering: start counting from most oxidized end (=at carbonyl group end)
- triose
- aldotriose
- D-glyceraldehyde
- L-glyceraldehyde
- ketotriose
- dihydroxyacetone (DHA)
- note: pyruvate is not a sugar
- aldotriose
- tetrose
- pentose
- aldopentose
- D-ribose
- furanose 5-ring
- 4C + O
- 1 external C
- furanose 5-ring
- D-ribose
- aldopentose
- hexose
- aldohexose
-
stereoisomers
- first and last carbon don't have 4 different groups
-
determines D/L
- D: right
- L: left
- remaining per class
- 8x D ("All altruists gladly make gum in gallon tanks")
- D-allose
- D-altrose
- D-glucose
- form
- linear=straight chain -> Fischer projection
- pyranose 6-ring -> Haworth projection
- 5C + O
- 1 external C
- closed with hemi-acetal
- aldehyde at C1
- alcohol: at C5
- C1 now also chiral
-
-D-glucose: at C1 down
- starch, glycogen
-
-D-glucose: at C1 up
- cellulose
-
-D-glucose: at C1 down
- conformations: chair vs boat
-
-glucosamine
- at C2
- form
- D-mannose
- D-gulose
- D-idose
- D-galactose
- D-talose
- 8x L (idem)
-
stereoisomers
- 2-ketohexose
- stereoisomers
- 4x D
- D-fructose
- two ring forms
- furanose 5-ring (most common)
- 4C + O
- 2 external C
- closed with hemi-ketal
- pyranose 6-ring
- furanose 5-ring (most common)
- two ring forms
- D-fructose
- 4x L (idem)
- aldohexose
- heptose
Disaccharides
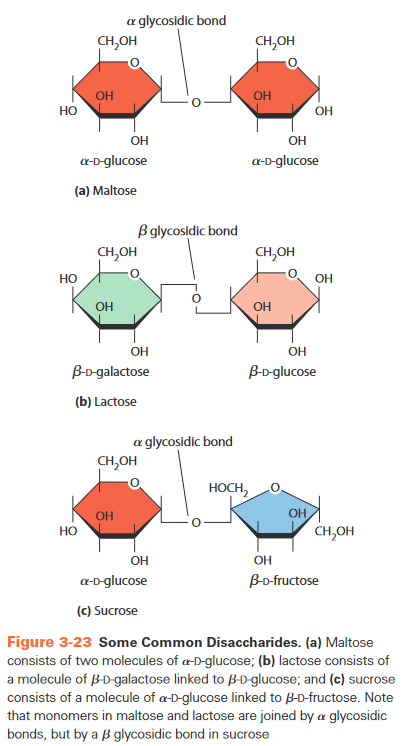
- covalent bonds
- condensation reaction
- glycosidic bond
- or depending on configuration of C1 in link
-
-glycosidic bond└┘
- maltose = -D-glucose + -D-glucose
- reducing? yes, at C1 of left glucose
- sucrose = -D-glucose + -D-fructose
- = saccharose
- reducing? no, because TODO
- maltose = -D-glucose + -D-glucose
-
-glycosidic bond |‾|_|
- lactose = -D-galactose + -D-glucose
- lactose intolerance: lack enzyme to break this bond
- reducing? yes, at C1 of left glucose
- lactose = -D-galactose + -D-glucose
Polysaccharides
- storage
-
-D-glucose polymers
-
bonds in backbone
- cf. maltose
- bonds form sidechains
- examples
- starch (plants)
- hydrophilic
- amylose (unbranched)
- hydrophobic
- amylopectin (branched)
- fewer longer branches
- ~80% of starch
- glycogen (animals and bacteria)
- many short branches
- hydrophilic
- starch (plants)
-
bonds in backbone
-
-D-glucose polymers
- structural
-
-D-glucose polymers
-
bonds
- mammals cannot hydrolyze this bond
- examples
- cellulose
- in cell walls of plants
- x36 -> microfibrils
- rigid, lineair rods
- hydrophobic
- cellulose
-
bonds
- bacteria cell wall
- alternating polysaccharide of
- N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc)
- N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc)
- alternating polysaccharide of
- chitin in exoskeletons
- GlcNAc only with bonds
-
-D-glucose polymers
Lipids
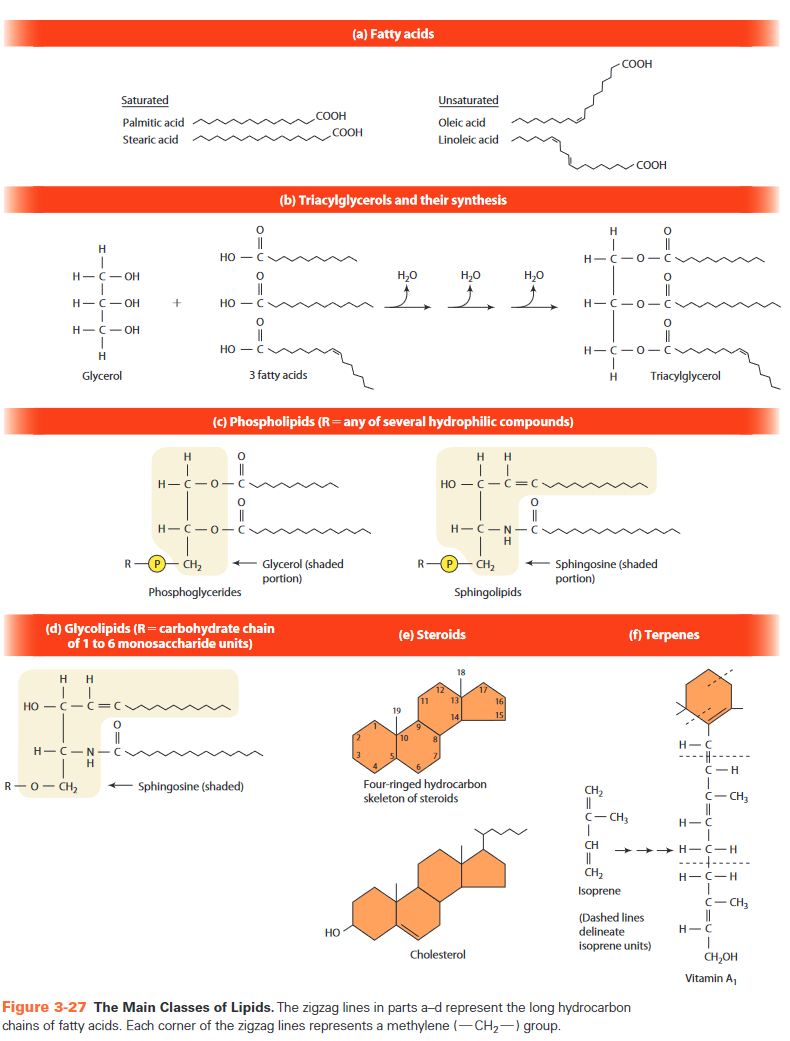
- hydrophobic or amphipathic
- not polymers in the classic sense
- six classes
- fatty acids
- building block
- amphipathic
- carboxyl group = head = hydrophilic
- hydrophobic tail
- 12-20 carbons (even)
- highly reduced (few oxygen atoms)
- high energy potential upon oxidation
- saturation
- saturated: no double bonds, max number of
- often animal fat
- solid at room temp
- often animal fat
- unsaturated
- one or more double bonds
- kink
- often vegetable oil
- liquid at room temp
- trans fats
- saturated: no double bonds, max number of
- triacylglycerols = triglycerides
- glycerol + 3 fatty acids
- glycerol:
- ester bonds
- condensation
- synthesis
- monoacylglycerol
- diacylglycerol
- triacylglycerol
- purpose
- energy store
- insulation
- hydrophobic
- glycerol + 3 fatty acids
- phospholipids
- amphipathic
- more than fatty acids
- in lipid bilayer membranes
- two types
- phosphoglycerides
- composed of
- glycerol
- 2 fatty acids
- 16-18 C
- same ester bond as triglycerides
- P
- hydrophilic group
- serine
- ethanolamine
- choline
- inositol
- composed of
- sphingolipids
- similar
- glycerol -> sphingosine
- only 1 fatty acid (up to 34 C)
- amide bond
- in lipid rafts
- phosphoglycerides
- amphipathic
- glycolipids
- similar to phospholipids
- P replaced by polysaccharide chain
- similar to phospholipids
- steroids
- hydrophobic
- four ringed skeleton
- variation in
- functional groups
- double bonds
- only in eukaryotes
- examples
- cholesterol
- amphipathic
- estrogen: estradiol
- androgen: testosterone
- glucocorticoid: cortisol
- mineralocorticoid: aldosterone
- cholesterol
- terpenes
- = isoprenoids (made from isoprene)
- vitamin A precursor
- fatty acids
- solubility
- triglycerides < fatty acids < phosphoglycerides
H5 Bioenergetics
- types of energy
- synthetic
- mechanical
- concentration
- electrical
- heat
- homeotherm (stable body temp)
- poikilotherm (fluctuating)
- light
- bioluminescence
- luciferine
- not: fluorescence
- phototrophy: light -> energy
- photo-autotrophy: photosynthesis in plants
- photo-heterotrophy: use light + organic molecules
- chemotrophy: oxidation -> energy
- chemo-autotrophy: anorganic molecules -> energy
- chemo-heterothrophy: macromolecules -> energy
- bioluminescence
- temperature
- [T] = K (not Celcius!)
- internal energy
- [E] = kcal/mol
- enthalpy/heat
- [H] = kcal/mol
- in biology: constant pressure, temp and volume
-
- : exotherm
- : endotherm
- entropy
- [S] = kcal/K
- 2nd law thermodynamics: (background info)
- spontaneity metric
-
- open systems can have decreasing entropy if compensated elsewhere
- increases with more disorder (TODO)
- split (hydrolysis, ...)
- better distribution (melting, evaporation, ...)
- ...
- Gibbs free energy
- [G] = kcal/mol
- : spontaneous to right, exergonic = energy-yielding
- : spontaneous to left, endergonic = energy-requiring
- minimal
- note: spontaneous != fast
-
- interpretation
- : more products
- : more reagentia
-
-> standard conditions
-
- also pH=7
-
- interpretation
- examples
- hydrophobic hydratation
-
large (+)
- because hydrophobic mix spontaneously with other hydrophobic elements
-
small (+)
- H bonds destroyed but also recreated
- so
-
large (+)
- oxidation of glucose under standard conditions
- : exotherm
- : spontaneous to right
- photosynthesis under standard conditions
- all signs reversed
- : not spontaneous
-
- cf.
- enzyme: phosphoglucoisomerase (PGI)
- part of glycolysis
-
- twice as much glucose as fructose in equilibrium
- cells keep steady state away from equilibrium using ATP
- [glucose-6-P] =
- [fructose-6-P] =
- hydrophobic hydratation
H5bis Bioenergetics
- druk
- [P] = Pa
- volume
- [V] = of L
- absolute temperatuur
- [T] = K
- hoeveelheid
- [n] = mol
- energie
- in cal
- energie vereist om 1g water met 1K te verhogen
- 1 J = 0.239 cal
- in cal
- gasconstante cal/(K mol)
- cal, niet kcal!
- moleculaire massa Da g/mol (molaire massa, bij benadering)
- concentratiebreuk voor
- evenwichtsconstante : waarde van bij evenwicht
- interne energie (soms ook )
- [E] = cal/mol (of J/mol)
- enthalpie
- [H] = cal/mol
- en constant in biochemie
- : exotherm
- : endotherm
- entropie
- [S] = cal/(K mol)
- cf. tweede hoofdwet thermodynamica:
- stijgt als
- betere verdeling
- splitsing in meerdere delen
- ...
- Gibbs vrije energie
- [G] = cal/mol
- : exergonisch, reactie naar rechts spontaan
- : endergonisch, reactie naar links spontaan
- minimaal
-
onder "standard temperature and pressure" (STP)
- T = 25 °C = 298.15 K
- P = 1 atm
- [P] = [R] = 1 M
- gasdichtheid bij STP: 22.4 L/mol
- onrealistisch in biochemie
-
- idem, plus pH = 7
- voor reactie
-
-
cal/mol
- enkel voor
- opgelet: in oef alles omzetten van kcal naar cal
-
cal/mol
- voorbeelden
-
- kcal/mol glucose
- kcal/mol
- kcal/mol
- hydrofobe hydratatie
- stijgt beetje
- stijgt veel
-
H6 Enzymes
- enzymes
- reusable, stay same before and after reaction
- help speed up catalysis
- bind all substrates to avoid relying on random collisions
- lower activation energy
- conformation change -> "bijna transitietoestand"
- surround substrates with strategic groups
- in context of enzymes
- reagentia = substrate
- binding site = active site
- enzyme-substrate interaction
- dissociation constant
- non-covalent
- affinity
- specificity
- lock-key (old) vs induced fit (new)
- co-factors = prosthetic groups
- metal ions
- co-enzymes = small organic molecules (vitamin derivatives)
- enzyme = apo-enzyme + co-enzyme
- acid-base catalysis
- protease: cleave proteins
- base attracts of away from binding site
- acid repels of towards binding site
- cf. Gly-2 and Gly-5
- lysozyme: covalent catalysis
- step 1: create covalent bond
- step 2: hydrolysis
- can cut bacterial cell wall (GlcNAc-MurNAc)
- sensitive to
- pH: changes charges of amino acid side chains
- ionic concentrations (e.g., salt)
- feedback: inhibition or activation
Classification
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzyme_Commission_number
- EC 1 oxidoreductases
- oxidation
- e.g., ethanol -> acetaldehyde
- (ignoring )
- paired reduction
- e.g.,
- extract
- proton from
- hydride ion from
- oxidation
- EC 2 transferases:
- often involve ATP
- EC 2.7 ~phosphotransferases ()
- = dephosphorylation + phosphorylation?
- EC 2.7.1 kinases
- EC 2.7.1.1 hexokinase
- EC 2.7.1.1 hexokinase
- EC 3 hydrolases: e.g.,
- EC 3.1 esterase:
- nuclease: nucleid acid hydrolysis
- cleave phosophodiester bonds
- ribonuclease (RNase) -> cleave RNA
- deoxyribonuclease -> cleave DNA
- lipase: fat hydrolysis
- EC 3.1.3 phosphatases: A-P + H2O -> A-OH + H-P
- reverse of kinase?
- EC 3.1.3.9 glucose-6-phosphatase
- nuclease: nucleid acid hydrolysis
- EC 3.2 glycosylases
- cleave polysaccharide bonds
- amylase: starch hydrolysis
- chitinase
- galactosidase
- lactase
- maltase
- sucrase
- EC 3.4 protease=peptidase
- cleave polypeptide bonds (proteolysis)
-
- splits into instead of
- EC 3.1 esterase:
- EC 4 lyases
- break covalent bond
- not using oxidation (else oxidoreductase)
- not using water (else hydrolase)
- EC 4.1.1.1 pyruvate decarboxylase
- EC 5 isomerases:
- move functional group within molecule
- outside would be transferase
- move functional group within molecule
- EC 6 ligases:
- use ATP to form covalent bond
- cf. ligand
- Latin: ligare = to connect
- [EC 7 translocases]
Enzyme kinetics
- also see notebook
- reaction speed
- depends on
- temperature
- constant in humans
- E activity
- <--
- temperature
- depends on
- Michaelis-Menten kinetics
- Michaelis-Menten constant
- measure for E-S affinity
- often near physiological [S]
- so small changes have big effect
- speed
- vs plot
- proof: see practicum 4
-
- initially linear
-
- levels off towards horizontal asymptote
-
- molecules (not moles!) converted per second for a single enzyme
- less enzymes, lower
- Michaelis-Menten constant
- Lineweaver-Burk plot
- linear
- vs
- Eadie-Hofstee plot
- linear
- vs
- Hanes-Woolf
Enzyme regulation
- enzyme inhibitors
- irreversible due to covalent bonds
- aspirine
- penicillin
- nerve gas (sarin, novichok): deactivate ACh-esterase
- but not all covalent bonds are irreversible
- e.g. phosphorylation
- reversible: non-covalent bonds
- competitive
- inhibitor binds on active site where substrate usually binds
- same
- higher/worse
- example: ethanol
- inhibits alcohol dehydrogenase breaking down ethylene glycol/methanol
- non-competitive
- inhibitor binds on different site
- same
- lower
- competitive
- irreversible due to covalent bonds
- allosteric control
- Greek: allosteric = other shape
- enzyme with 2 forms: high and low affinitiy
- inhibition
- often multi-subunit: catalytic and regulatory subunit
- often first enzyme of cascade -> feedback inhibition
- competitive or non-competitive
- all non-competitive inhibitors are allosteric
- activation
- cooperativity
- positive or negative
- e.g. myoglobin and hemoglobin
- oxygen saturation vs oxygen partial pressure: sigmoid curve
- opens up when more oxygen bound -> positive
- covalent modifications
- phosphorylation
- binding one or more P can activate some enzymes
- e.g., glycogen phosphorylase a and b (in cytosol)
- e.g., protease activation in small intestine via trypsin + enterokinase
- phosphorylation
- misc
- RNA catalysis: ribozymes
H9 Glycolysis and fermentation
- adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
- A-P~P~P
- 1 phosphoester bond
- 2 phosphoanhydride bonds
-
- real life: [ATP] 5:1 [ADP]
-
- 1 phosphoester bond
- hydrolysis:
- reverse: condensation
- energy rich bond
- = highly exergonic hydrolysis
- charge repulsion between P groups
- resonance stabilization
- cf.
- spread over 4 atoms in
- optimal, low energy
- when bound: spread over 3, higher energy
-
- spatial randomization
- more soluble
- A-P~P~P
- oxidation = dehydrogenation (in organic chemistry)
- oxidation: donate electron
- typically by donating entire hydrogen atom
- always in pairs
-
- extract proton () + hydride ion ()
- reduction = hydrogenation
- nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide ()
- co-enzyme
- electron acceptor
- contains 1 adenosine as in RNA
- AMP
- other ribose bound to nicotinamide
- nicotinamide can be reduced by hydrogenation
- pyrophosphate bridge: s linked to each other
- not to riboses as in DNA/RNA
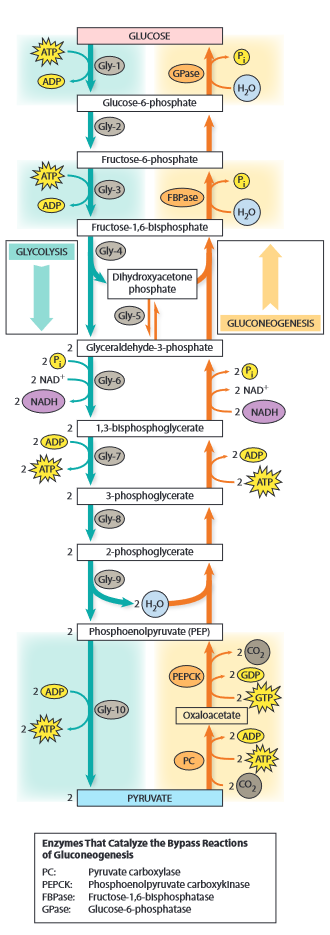
Glycolysis
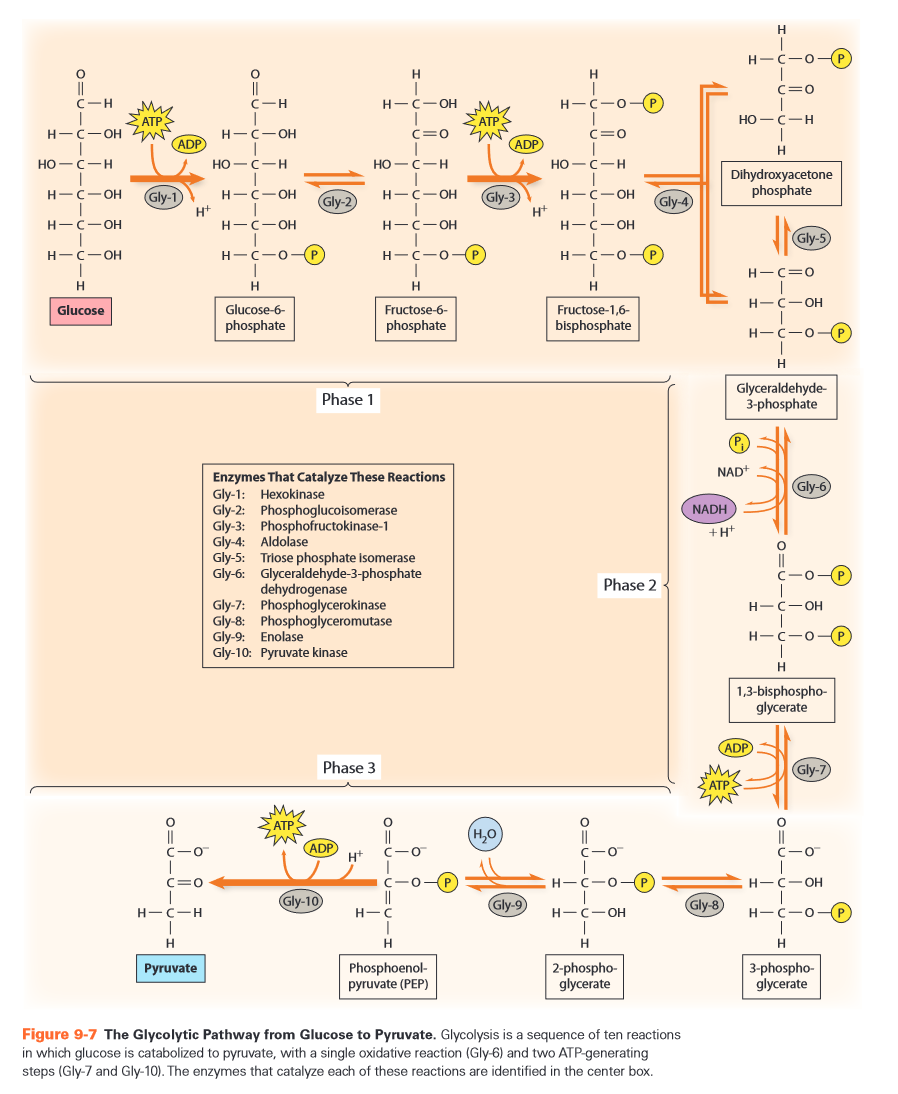
- in cytosol
- anaerobic
- partial oxidation of glucose to pyruvate
- abbreviations
- G6P = glucose-6-P
- F6P = fructose-6-P
- F1,6BP = fructose-1,6-bisP
- DHA = dihydroxyacetone (ketotriose)
- DHAP = DHA phosphate
- GA3P = glyceraldehyde-3-P
- 1,3-BPG = 1,3 bisP-glycerate
- 3-PG = 3-P-glycerate
- 2-PG = 2-P-glycerate
- PEP = Penol-pyruvate
| Step | Enzyme | Abbr | Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gly-1 | hexokinase | EC 2.7.1.1 (phospho)transferase | |
| Gly-2 | phospho-gluco-isomerase | GPI | EC 5.3.1.9 isomerase |
| Gly-3 | phospho-fructokinase-1 | PFK-1 | EC 2.7.1.11 (phospho)transferase |
| phospho-fructokinase-2 | PFK-2 | EC 2.7.1.x (phospho)transferase | |
| Gly-4 | aldolase | EC 4.1.2.13 lyase | |
| Gly-5 | triose phosphate isomerase | TPI | EC 5.3.1.1 isomerase |
| Gly-6 | GA3P dehydrogenase | GAPDH | EC 1.2.1.12 oxidoreductase |
| Gly-7 | phosphoglycerokinase | PGK | EC.2.7.2.3 (phospho)transferase |
| Gly-8 | phosphoglyceromutase | PGM | EC 5.4.2.11 isomerase |
| Gly-9 | enolase | EC 4.2.1.11 lyase | |
| Gly-10 | pyruvate kinase | EC 2.7.1.40 (phospho)transferase | |
| E1 | starch phosphorylase | EC 2.x.x.x transferase | |
| E2 | glycogen phosphorylase | EC 2.x.x.x transferase | |
| E3 | galactokinase | EC 2.7.1.6 (phospho)transferase | |
| E4 | uridyl transferase | EC 2.x.x.x transferase | |
| E5 | UDP-galactose epimerase | EC 5.1.3.2 isomerase | |
| E6 | UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase | EC 2.x.x.x transferase | |
| E7 | phosphoglucomutase | EC 5.4.2.2 isomerase | |
| E8 | lactase | EC 3.2.1.108 hydrolase | |
| E9 | maltase | EC 3.2.1.20 hydrolase | |
| E10 | sucrase | EC 3.2.1.x hydrolase | |
| E11 | hexokinase | EC 2.7.1.1 (phospho)transferase | |
| E12 | phosphomannoisomerase | EC 5.x.x.x isomerase | |
| E13 | glycerokinase | EC 2.7.1.30 (phospho)transferase | |
| E14 | glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | EC 1.1.1.8 oxidoreductase | |
| Gng-1 | glucose-6-phosphatase | GPase | EC 3.1.3.9 hydrolase |
| Gng-3 | fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase | FBPase | EC 3.1.3.11 hydrolase |
| Gng-10 | pyruvate carboxylase | PC | EC 6.4.1.1 ligase |
| Gng-10 | phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase | PEPCK | EC 4.1.1.32 lyase |
| FERM | lactate dehydrogenase | LDH | EC 1.1.1.27 oxidoreductase |
| FERM | pyruvate decarboxylase | PDC | EC 4.1.1.1 lyase |
| FERM | alcohol dehydrogenase | ADH | EC 1.1.1.1 oxidoreductase |
- 10 step process
-
- problem if supply is depleted
- recover in later stage (fermentation or aerobic respiration/ETS)
- phase 1 (Gly1 - Gly5)
- cleave sugar by double phosphorylation
- Gly-1:
- hexokinase = kinase for hexoses
- ATP: energy + P donor
- Gly-2:
- aldose-ketose isomerase
- using acid-base catalysis
- move s around
- Gly-3:
- Gly-4:
- split hexose in two trioses
- DHA: ketotriose
- GA: aldotriose
- split hexose in two trioses
- Gly-5:
- aldose-ketose isomerase
- using acid-base catalysis
- cf. Gly-2
- phase 2 (Gly6 - Gly7)
- count everything double from here on
- Gly-6:
- dehydrogenation of aldehyde
- using Cys with group
- "covalent catalytic intermediary"
- create energy rich bond ~
- Gly-7:
- phase 3 (Gly8 - Gly10)
- Gly-8:
- Gly-9:
- Gly-10:
- Gly-10a:
- Gly-10b:
- enolpyruvate is unstable
- all steps except 1, 3, 10 are reversible
- steps 1,3,7,10 involve phosphokinases
- steps 1,3 require ATP
- steps 7,10 yield ATP
- steps 2,5 uses acid-base catalysed aldose-ketose isomerase
- step 4 splits the hexose -> lyase
- steps 5,8 move P around -> isomerases
- step 6 is actual oxidation -> oxidoreductase, using Cys E-SH
- types of enzymes
- kinases = transferases: 4
- isomerases: 3
- lyases: 2 (aldolase, enolase)
- oxido-reductase: 1 (GAPDH)
-
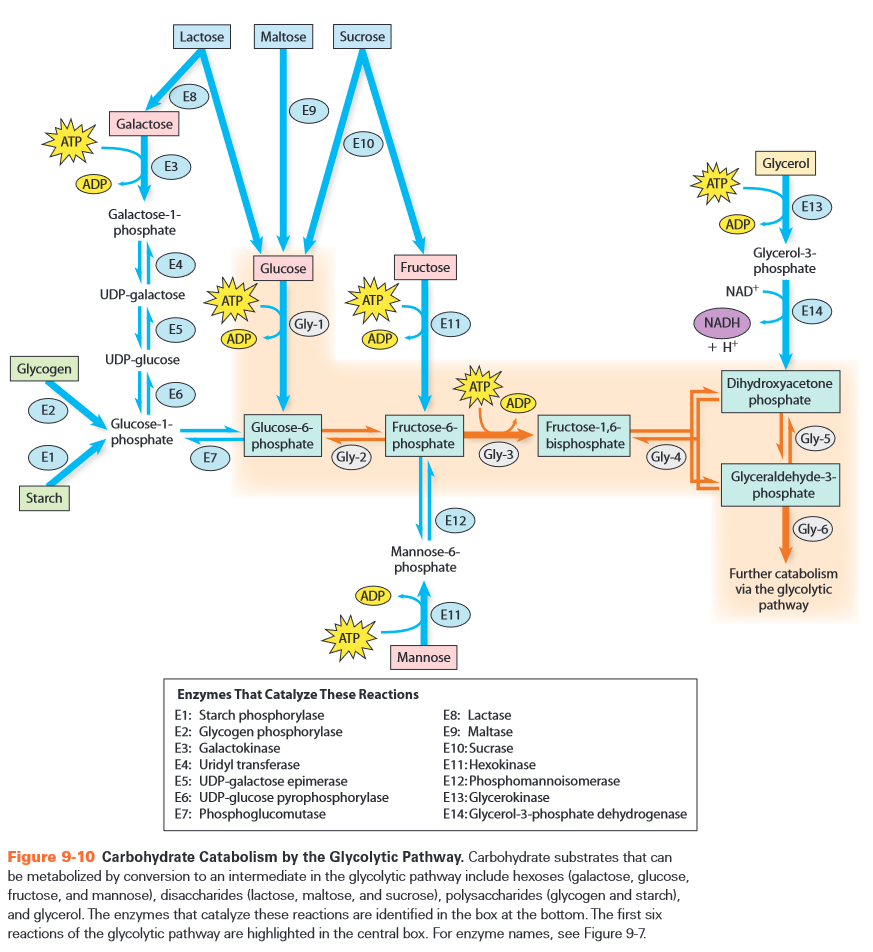
- alternative substrates
- monosaccharides
- glucose -> G6P -> F6P
- fructose -> F6P
- mannose -> M6P -> F6P
- galactose -> Ga1P -> ... -> G1P -> G6P -> F6P
- hydrolize disaccarides
- humans always hydrolise
- bacteria can cleave by phosphorylation
- cf. polysaccharides below
- sucrose -> G6P + F
- more efficient (saves 1 ATP)
- phosphorylate polysaccharides to split of G1P
- only path where no initial ATP is required
- glycoside bonds release enough energy when hydrolysed
- always ATP required to phosphorylate each monosaccharide
- exception: polysaccharides
- glycerol
- monosaccharides
- gluconeogenesis
- in liver
- start from lactate or pyruvate
- reverse of glycolysis
- except for 3 irreversible steps (1,3,10)
- Gng-1:
- Gng-3:
- Gng-10
- expensive step
- Cori cycle
- glycolysis and fermentation in muscles
- gluconeogenesis in liver
- neutral operations on both sides
- gain 2 ATP, lose 6 ATP
- glycolysis and fermentation in muscles
Fermentation
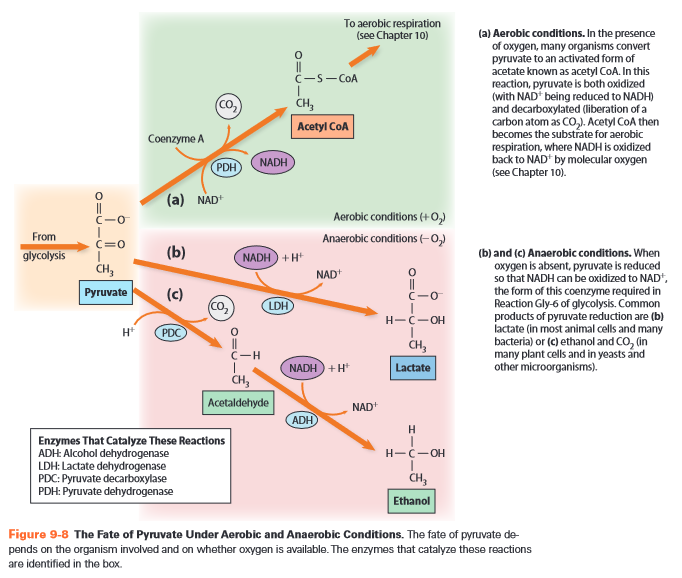
- anaerobic
- recovers
- works for most sugars except pentoses and lactose
- two options
- pyruvate -> lactate
- pH decreases -> enzyme activity decreases
- LDH = lactate dehydrogenase = oxidoreductase
- pyruvate -> ethanol + CO2
- PDC = pyruvate decarboxylase = EC 4.1.1.1 lyase
- ADH = alcohol dehydrogenase = oxidoreductase
- 17g sugar -> 1% alcohol
- pyruvate -> lactate
- efficiency of glycolysis thus far (under standard conditions)
-
-
- of free energy in glucose remains after glycolysis
- free energy consumed
- energy created: 2 ATP
- efficiency:
- 2% of total free energy in glucose
-
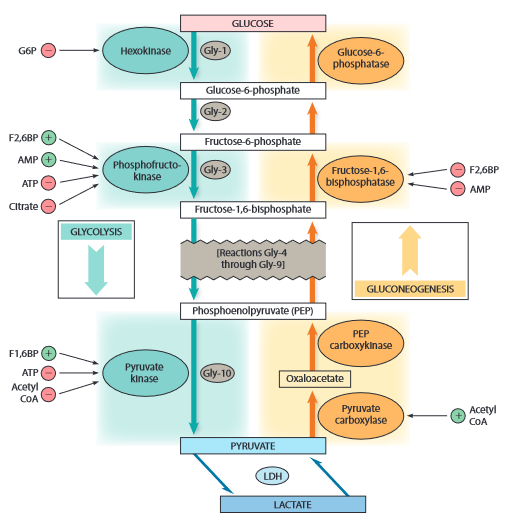
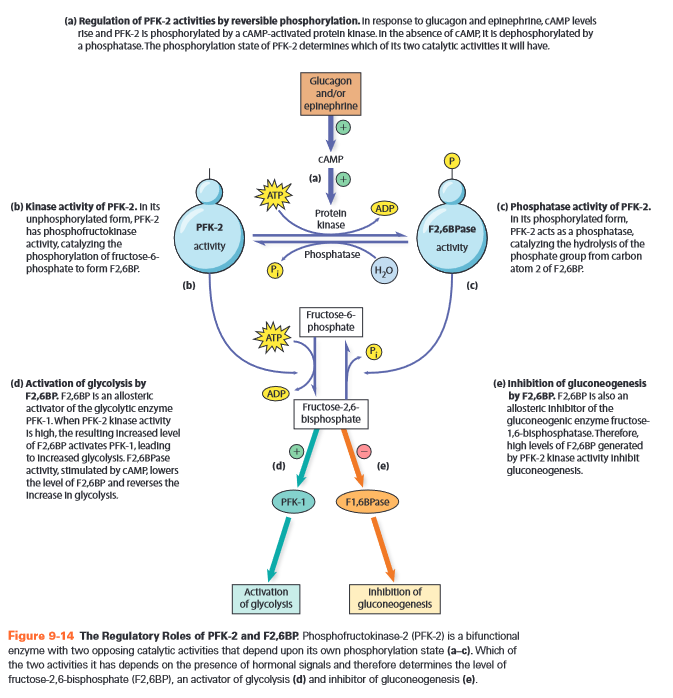
Regulation
- allosteric regulation
- affects irreversible steps 1,3,10
- Gly-1: hexokinase
- G6P -
- Gly-3: PFK-1
- F2,6BP +
- AMP +
- ATP -
- citrate -
- Gng-3: FBPase
- F2,6BP -
- AMP -
- Gly-10: pyruvate kinase
- F1,6BP +
- ATP -
- Acetyl CoA -
- Gng-10: PC
- Acetul Coa +
H10 Aerobic respiration
- in mitochondria
- cf. glycolyse in cytosol
- exception: in membrane+cytosol for bacteria
Mitochondria
- mitochondria
- outer membrane (7nm)
- contains porines
- max 5 kDa: glucose, ATP, protein <50 AA
- made from sheets
- contains porines
- intermembrane space
- lots of H+
- pH - 1
- inner membrane
- cristae
- increase inner membrane surface
- cristae
- matrix
- (circular) DNA + ribosomes
- outer+inner membrane connect sometimes
- outer membrane (7nm)
- goals
- complete breakdown of pyruvate
- 38 ATP
- recover NAD+
- complete breakdown of pyruvate
- pyruvate flow
- through porines of outer membrane
- transport through inner membrane
- phase 1: pyruvate to Acetyl CoA
- in matrix
- oxidative decarboxylation: remove CO2
- CoA = co-enzyme A
- ~= AMP + pantothenic acid (vitamin B5)
- HS-CoA vs Acetyl CoA
- sulfhydryl vs thio-ester
-
- once for each pyruvate
- thiamine = vitamin B1
- two irreversible steps
- add
- release
- 3C -> 2C
- two reversible steps
- oxidation with
- create energy rich bond ~
- oxidation with
- pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH)
- inactivate when phosphorylated
- regulation
- down when plenty of energy or products
- ACoA
- NADH
- ATP
- up when low on energy or many substrates
- CoA
- NAD+
- AMP
- down when plenty of energy or products
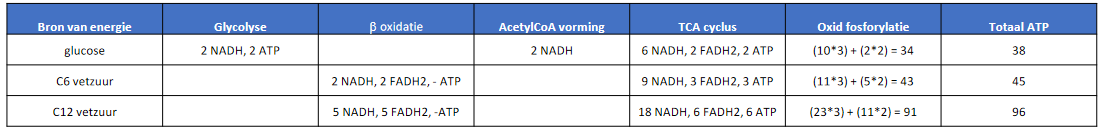
Citric acid cycle
- phase 2: citric acid cycle = Krebs = TCA
- in matrix
- once for each pyruvate/ACoA
- common molecules
- oxaloacetate: 4C
- acetyl CoA: 2C
- citrate: 6C
- alpha-ketoglutarate: 5C
- succinyl CoA: 4C
- succinate: 4C
- fumarate: 4C
- malate: 4C
- 4 + 2 = 6
- 6 - 1 = 5
- 5 - 1 = 4
- 8 steps (each individually irreversible)
- CAC-1:
- combinating decreases
- must be compensated with from ~
- CAC-2:
- switch H and OH group
- CAC-3:
- CAC-4:
- cf. pyruvate -> ACoA
- CAC-5:
- GTP used to ADP->ATP
- succinate = barnsteenzuur
- CAC-6:
- remove 2H, add double bond
- fumarate: : highly dehydrogenated
- FAD = flavin adenine dinucleotide
- co-enzyme
- cf. NAD+
- AMP + P + riboflavin
- riboflavin
- ~vitamin B
- 3 6-rings
- oxidized (without H) or reduced ()
- CAC-7:
- malate = appelzuur
- CAC-8:
- regulation
- always during oxidation=dehydrogenation with NAD+ (not FAD)
- CAC-3: ICDH
- NADH -
- ADP +
- CAC-4: KGDH
- NADH -
- Succinyl CoA -
- CAC-8: MDH
- NADH -
- summary
- oxidative decarboxylation in CAC-3,4
- single ATP gained in CAC-5
- CAC-6 uses FAD instead of NAD+
- 2 CO2 are actually released from of citrate, not from ACoA
- enzym classes
- 4 oxidoreductases = dehydrogenases (5 when including PDH)
- 2 lyase
- 1 transferase?
- 1 ligase
| Step | Enzyme | Abbr | Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| pyruvate dehydrogenase | PDH | EC 1.2.4.1 oxidoreductase | |
| CAC-1 | citrate synthase | CS | EC 2.3.3.1 transferase (former lyase?) |
| CAC-2 | aconitase | EC 4.2.1.3 lyase | |
| CAC-3 | isocitrate dehydrogenase | ICDH | EC 1.1.1.42 oxidoreductase |
| CAC-4 | ketoglutarate dehydrogenase | KGDH | EC 1.x.x.x oxidoreductase |
| CAC-5 | succinyl CoA synthetase | SCS | EC 6.2.1.4 ligase |
| CAC-6 | succinate dehydrogenase | SDH | EC 1.3.5.1 oxidoreductase |
| CAC-7 | fumarate hydratase | FH | EC 4.2.1.2 lyase |
| CAC-8 | malate dehydrogenase | MDH | EC 1.1.1.37 oxidoreductase |
- note: enzyme mostly contains name of substrate, rarely product
- exceptions: CAC1,2
Fat metabolism
- triglyceride = glycerol + fatty acid
-
in glycolysis
- 2 steps
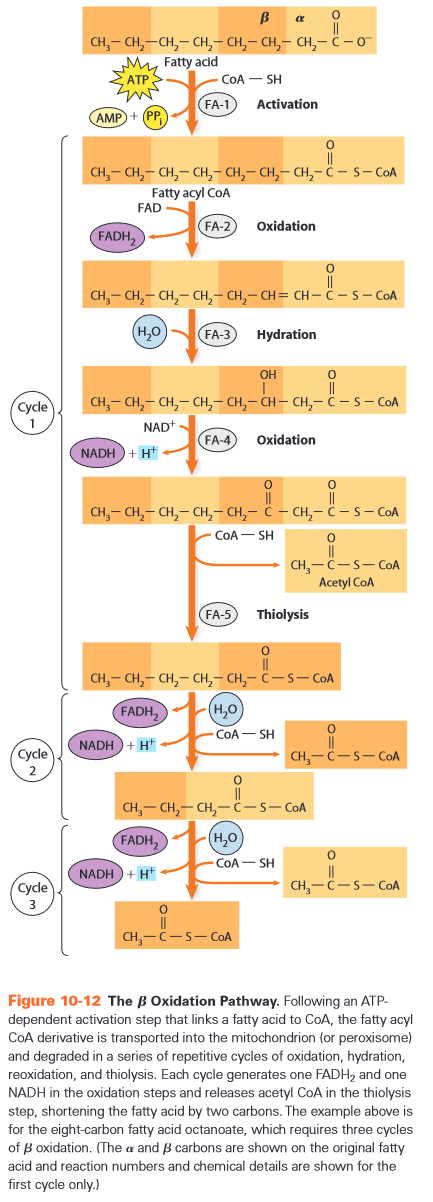
- 2nC fatty acids -> -oxidation to n ACoA -> CAC -> n ATP
- in matrix
- = head of fatty acid =
-
= right after head
- gets oxidized to to form new head later
- FA-1: activation
- costs 2 phosphoanhydride bonds
- creates high energy bond ~
- does not get used immediately?
- rest in n-1 cycles of 4 steps
- remove 2C as ACoA every cycle
- FA-2: oxidation (FAD)
- FA-3: hydration (H2O)
- FA-4: oxidation (NAD+)
- FA-5: thiolysis
- process can deplete free CoA when lots of fat is burned
- halts CAC
- fat -> ketone bodies (partial oxidation)
- fat -> 2 ACoA -> Acetoacetyl CoA -> Acetoacetate
- heart and brain can consume ketone bodies
- can lower blood pH -> ketoacidosis -> health risk?
-
in glycolysis
Protein metabolism
- protein -> AA
- endoprotease and exoprotease
- reuse for protein synthesis
- or break down to generate ATP
- AA -> alpha-keto acid + ureum
- remove amino group
- Ala <-> pyruvate -> CAC
- Asp <-> oxaloacetate -> CAC
- Glu <-> alpha-ketogluterate -> CAC
- CAC is amphibolic: connects anabolic + catabolic
- AA -> alpha-keto acid + ureum
Misc
- glyoxylate cycle
- fat -> sugar
- only in plants
- in glyoxosome
- (triglycerides -> )ACoA -> succinate -> PEP -> sugar
- details not important
Electron transport chain/system (ETS)
- inner membrane proteins
- reminder: oxidation = donating electrons
-
: standard reduction potential (in Volt)
- cf. standard conditions for
- spontaneity of redox reaction
- e acceptor -> reduce
- e donor -> oxidize
-
- minus -> opposite signs
- number of electrons
- Faraday constant
-
-
- can be reduced:
-
- reduced form, can be re-oxidized to
-
-
- electron carriers
- flavo (FAD, FMN): p + e
- FMN = flavo mono nucleotide
- Fe-S: only e
- cytochrome (heme): only e
- Cu cytochrome: only e
- coenzym Q (CoQ) = ubiquinon: p + e
- not a protein
- 6-ring with =O at top and bottom
- CoQ <-> CoQH <-> CoQH2
- acts as pump
- on inside
- on outside
- four respiratory complexes
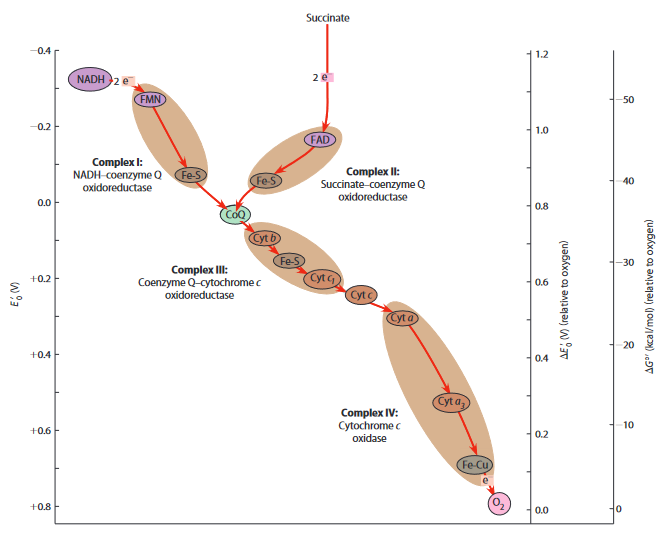
- goal: increase towards step by step
- organized in supercomplexes = respirasomes
- Q cycle not important
- complex I: NADH-CoQ ORase
- complex I pumps
- complex II: succinate-CoQ-ORase
- alternative to complex I with FAD instead of NADH
- does not pump
- complex III: CoQ-cytochrome c ORase
- CoQ pumps
- complex III pumps
- total: from matrix to intermembrane space
- complex IV: cytochrome c oxidase
- complex IV pumps
- cyanide and azide could bind and block this process
- incomplete reduction of O2
- if complex I or III transfer e to O2
- -> toxic superoxide anion
- or
- if complex I or III transfer e to O2
- result
- NADH oxidation: 4+4+2=10H+
- FAD oxidation: 4+0+2=6H+
- flavo (FAD, FMN): p + e
-
ATP synthase
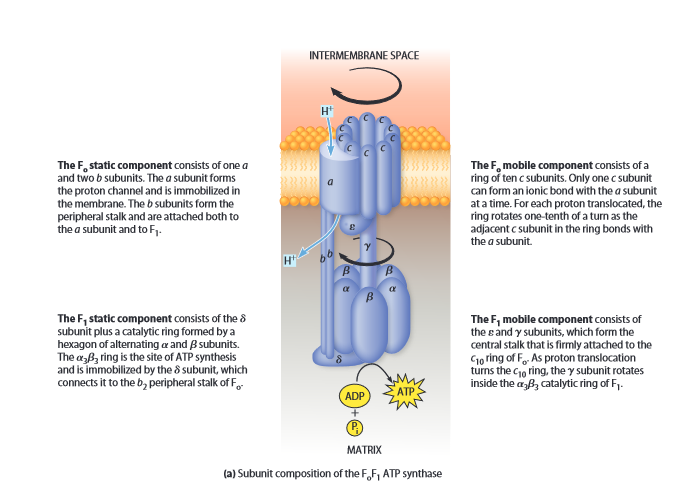
- also in inner membrane
- proton channel: intermembrane space -> matrix
- converts 1 ADP -> 1 ATP per 3-4 protons
- proton motive force (pmf)
-
- dus ?
-
: proton translocator
- subunit a x1
- channel
- subunit b x2
- stalk connecting F0 with F1
- subunit c x10
- 1 of 10 has ionic bond with a (Asp-Arg)
- proton neutralizes Asp
- rotates 1/10 per proton
- turns
- subunit a x1
-
: create ATP from proton gradient
- subunit x3
- forms hexagon
- subunit x3
- ATP synthesis
- 3 conformations
- open
- loose
- tight: ADP + P -> ATP
- instead of
- subunit x1
- link b with hexagon
- subunit x1
- stalk
- rotates to transmit energy from F0 to F1
- subunit x1
- links to c-ring
- also rotates
- subunit x3
- uncouplers
- e.g., dinitrophenol (DNP) or thermogenine
- bind with protons -> no gradient
- transfer back across membrane
- oxygen still consumed
- but no ATP synthesis
- e.g., dinitrophenol (DNP) or thermogenine
- final result per glucose
- 34 is best case scenario
- alternative: NADH -> shuttle
- -> liver, heart, kidney: 3 ATP
- -> muscle, brain: 2 ATP
- pmf can also be used elsewhere
- alternative: NADH -> shuttle
- total: 36-38ATP
- ATP hydrolysis: 10 - 14 kcal/mol
- let's say 10
- times 38 -> 380 kcal/mol
- compare with glucose:
- ~55% efficiency
- result for other inputs
- NADH ->[ETS] 3 ATP
- FADH2 ->[ETS] 2ATP
- ACoA ->[TCA] 1 ATP + 3 NADH + 1 FADH2 ->[ETS] 12 ATP
- notes
- GTP in 3 places
- Gng-10: oxaloacetate -> PEP
- CAC-5: succinyl-CoA -> succinate
- (later) importin/exportin with RAN
- FAD in 2 places
- beta oxidation: first of two oxidations
- CAC: succinate -> fumerate
- ligase enzyme in 2 places
- Gng-10: puryvate carboxylase to create oxaloacetate
- CAC: succinyl CoA synthetase
- GTP in 3 places
- TODO create Excel of ATP per substance like in WZ3
H11 Photosynthesis
- endosymbiosis (like mitochondria)
- in chloroplast
- stroma
- thylakoid
- membrane ~= inner membrane mitochondria
- lumen ~= intramembrane space mitochondria -> H+ gradient
- stack = granum
- two processes
- transduction: light -> chemical energy
- photosystem I and II
- coupled by electron transport chain
- electron source: water
- electron acceptor: , not
- F0F1 ATPase
- photosystem I and II
- create carbohydrates from from CO2 and H2O
- Calvin cycle
- ribulose
- Calvin cycle
- transduction: light -> chemical energy
H16 DNA and chromosomes
16.1 Genetic material
- experiment: pneumococcus R <-> S in mice
- heat killed S + living R -> living S -> dead
- protease -> no
- RNAse -> no
- lipase -> no
- sacharase -> no
- DNAse -> yes
- (bacterio)faag
- lytische cyclus: vermenigvuldigen
- lysogene cyclus: integreeg DNA in gastheer, inactief
- experiment: vs
- -> DNA
- niet in mantel
- wel in sommige kopieen
- S in proteinen (Cys of Met), dus enkel in mantel
- RNA faag
- Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV)
- Ribgrass Mosaic Virus (RMV)
- RNA TMV + mantel RMV = TMV
- retrovirus
- HIV
- 2x (+)ssRNA?
- reverse transciptase: RNA -> DNA
- HIV
- +ssRNA
- TMW
- COVID-19
- -ssRNA
- influenza
- dsDNA
- HPV
16.2 DNA structure
- TODO
- see handwritten notes
16.3 DNA packing
- TODO
- see handwritten notes
16.4 Nucleus
- TODO
- see handwritten notes
H17 DNA replication and error correction
- TODO
- see handwritten notes
H18 transcriptie
- TODO
- volgorde mRNA maturatie
- transcriptie initiatie (reminder: 5'->3')
- toevoegen van 5’ cap
- pre-mRNA-splicing
- introns weg
- toevoegen van poly-A staart
- transport naar het cytoplasma
H19 translatie
- TODO
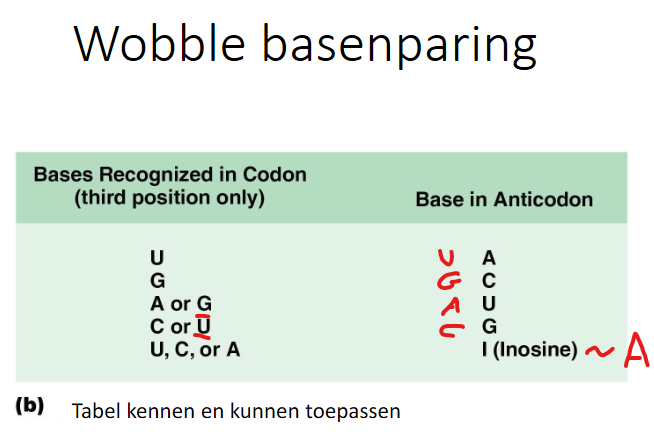
- voorbeelden van hoe cel omgaat met nonsense/nonstop mutatie in mRNAs
- (1) suppressor tRNAs
- bv. nonsense suppressor tRNA
- (2) nonsense gemedieerde mRNA afbraak (NMD)
- (3) nonstop mRNA decay
- (1) suppressor tRNAs
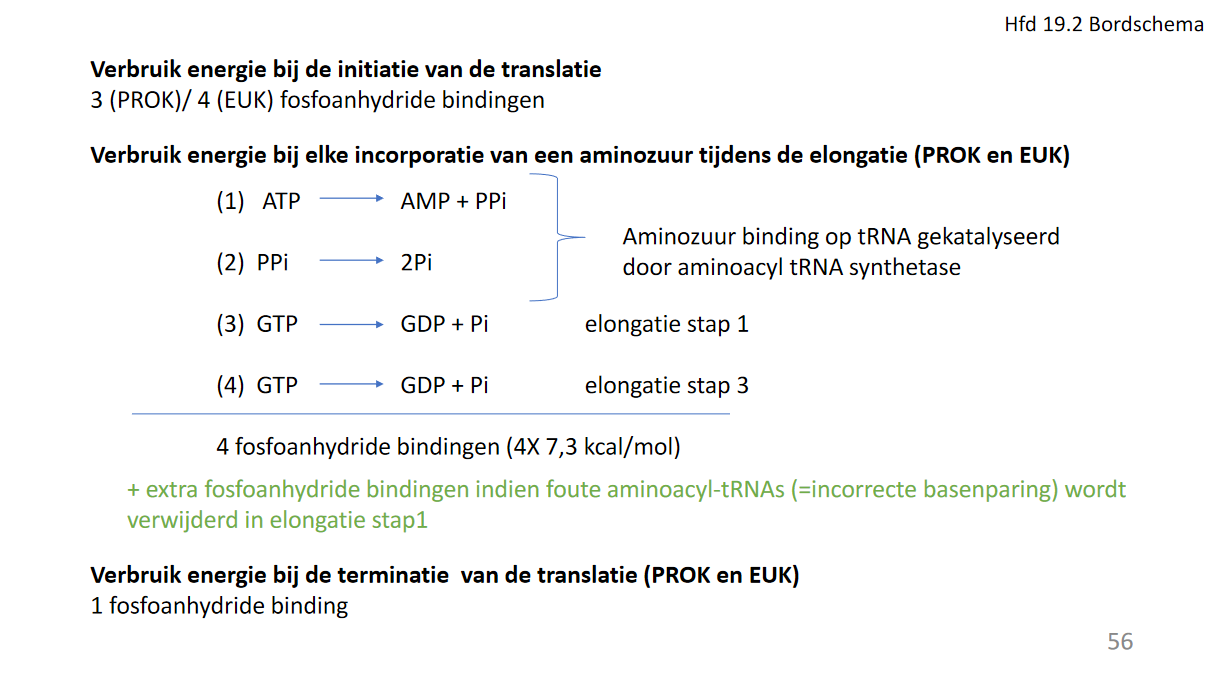
- energieverbruik (fosfoanhydride) translatie
- initiatie
- prokaryoot: 3
- eukaryoot: 4
- elongatie: 4/AZ
- ATP -> AMP
- 2GTP -> 2GDP
- extra bij fouten
- terminatie: 1
- initiatie
H20 regulatie
- TODO
H21 methods
- TODO
- blots
- southern: DNA
- northern: RNA
- western: protein
H24 mitose
- mitose (2n/4C -> 2n/2C)
- profase
- chromosomen
- 2xMTOC met elk 2 centriolen
- prometafase
- microtubuli
- kinetochoor -> chromosomen
- polair (pool-pool)
- astraal (pool-membraan)
- microtubuli
- metafase
- chromosomes in metaphase plate
- anafase
- afbraak cohesin
- anafase A)
- kinetochoor MTs korter
- kinesine aan + (chromosoom) uiteinde
- ander kinesine aan - (centrosoom)
- zusterchromatiden uit elkaar
- kinetochoor MTs korter
- anabase B)
- polaire MTs langer
- polen uit elkaar
- bipolaire kinesine
- polaire MTs langer
- astrale MTs korter
- dyneinen
- telofase
- chromosoom decondensatie
- nucleoli verschijnen
- kernmembraan wordt gevormd
- begin cytokinese
- cytokinese
- contractiele actine-microfilamenten
- contractiele ring: Interactie actine – myosine
- myosine niet nodig voor mitose zelf
- prokaryoten
- FtsZ eiwit
- profase
- regulering mitose
- cycline-afhankelijke eiwitkinasen (Cdk)
- growth factors (GFs)
- 3 checkpoints = transitiepunten
- G1/S
- S-fase: replicatie licensing
- MCM (DNA helicase) complex verwijderd
- S-fase Cdk -> fosforylering van ORC + helicase laders -> max 1 copy
- geminine
- G2/M
- meta/ana
- anafase-promoting complex (APC)
- apoptosis
- != necrose
- caspase
- Bcl2 (anti-apoptosis) inhibited
- DNA damaage -> p53 -> inhibit Blc2
- GF -> ... BAD -> inhibit Bcl2
H25 meiose
- asexual reproduction
- parthenogenese: 1 unfertilized gamete -> embryo
- meiose
- 1 diploid -> 4 haploid
- meiose I (2n/4C -> 1n/2C)
- pro I
- leptotene
- zygotene
- start homologous chromosomes synapsis
- "bivalent"
- between non-sister chromatids
- non-uniform -> hotspots
- start homologous chromosomes synapsis
- pachytene
- start crossing over
- diplotene
- chiasmata due to crossing over shows
- achiasmy: in male fruit flies
- synaptonemal complex dissolves
- chiasmata due to crossing over shows
- diakinesis
- meta I
- ana I
- scheiding homologen
- bv. X-Y uit elkaar
- zusterchromatiden nog wel samen
- shugoshin -> geen afbraak cohesin
- scheiding homologen
- telo I
- cytokinese
- two haploid daughter cells
- pro I
- interfase zonder S-fase
- meiose II (1n/2C -> 1n/1C)
- pro II
- meta II
- ana II
- telo II + cytokinesis
- non-disjunction
- euploid: OK
- aneuploid
- -somie
- 1 chromosoom
- monosomie
- trisomie
- 21 -> Down
- XXY: Klinefelter
- XYY
- XXX
- X: Turner
- polyploid
- alle chromosomen
- triploid (3n)
- tetraploid (4n)
- -somie
- oogenese
- 4 haploid
- 1 eicel
- 3 poollichamen
- pauze pro I (foetus 7md)
- meta II arrest (tot bevruchting)
- 4 haploid
- Mendel
- gen met 2 varianten (= allelen)
- homozygoot (YY of yy)
- heterozygoot (Yy)
- dominant (Y)
- recessief (y)
- genotype vs fenotype
- Punnett square
- sikkelcel: recessief, 1/4 kans
- recombinatie
- cf. H17
- Spo1: endonuclease voor dsDNA
- Rad51: ssDNA ligase
- bronnen variatie
- pro I: crossing over
- ana I: splitsing homologen
- types in bacteria
- translation
- transduction by phage
- conjugation by sex pilus + F plasmid
H26 kanker
- TODO
Practicum 1 - fotometrische dosage van eiwitten
- wet Lambert-Beer
- absorbantie
- laagdikte
- concentratie [mg/ml]
- intredend licht
- uittredend licht
- extinctiecoefficient
- karakteristiek voor product
- mate van absorptie voor bepaalde golflengte
- hier:
-
- stijgt -> daalt
- linear verband zwakt af bij hogere concentraties
Practicum 2 - DNA: structuur, amplificatie en restrictiedigestie, gelelektroforese
- structuur: zie theorie
- amplificatie
- PCR
- materiaal
- template DNA om te vermenigvuldigen
- primers: ssDNA
- dNTPs: bouwstenen (dATP, dTTP, dCTP, dGTP)
- Taq DNA polymerase (hitteresistent)
- buffer
- cyclus (elke 90s)
- DNA denaturatie
- verwarm tot 94°C
- primer hybridisatie / annealing
- verlaag temp tot 58°C
- primers binden met template DNA
- DNA elongatie
- verhoog tot 72°C
- polymerase bouwt het DNA vanaf 3' van primers verder op
- DNA denaturatie
- herhaal keer
- practicum: 25
- praktijk: veel meer
- aantal kopieen:
- restrictie-digestie
- doel: knip DNA op specifieke plaats
- a.h.v. restrictieenzymen = endonucleasen
- op 37°C
- hier: knip dsDNA in (circulair) plasmide (pGem-T)
- gelelektroforese
- doel: lengte DNA fragmenten bepalen
- agarose gel
- niet geladen
- polair
- poeder + buffer -> koken -> afkoelen -> polymeriseren, crosslinks
- elektro -> elektrisch veld
- DNA negatief -> gaat naar positieve pool
- korter -> minder hinder door aragose -> verder
- laadbuffer: hoge dichtheid + kleurstof om visueel verloop te volgen
- DNA ladder: DNA met bekende lengte als controle
- na 30min
- SYBR Safe toevoegen
- bindt aan DNA -> fluorescent bij UV licht
Practicum 3 - koolhydraten en lipiden
- reducerend vermogen van suikers (Benedict test)
- oxidatie van aldohexose:
- reductie
- (+II to +I)
- test per suiker
- glucose: ja
- fructose: ja
- sucrose: nee
- lactose: ja
- glycogeen: nee
- hydrolyse van disacchariden
- zure hydrolyse:
- herhaal test
- sucrose -> glucose + fructose: ja
- glycogeen: ?
- herhaal test
- enzymatische hydrolyse: bv. amylase voor zetmeel
- skipped
- zure hydrolyse:
- fermentatie
- extractie lipiden uit melk
- vooral triacylglycerol
- 2/3 verzadigd
- volle melk: 3.5% vet
- halfvolle melk: 1.5% vet
- vooral triacylglycerol
Practicum 4 - enzymkinetica
- theorie: H6 Enzymes
- zie notebook
- enzym: alkaline phosphatase
- class EC 3.1.3.1 -> hydrolase
Practicum 5 - structuur macromoleculen
- toepassing theorie